-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 10
Stacked Alternating Offers Protocol
According to this protocol [1], all of the participants around the table get a turn per round; turns are taken clock-wise around the table. The first party starts the negotiation with an offer that is observed by all others immediately. Whenever an offer is made the next party in line can take the following actions:
- Make a counter offer (thus rejecting and overriding the previous offer)
- Accept the offer
- Walk away (e.g. ending the negotiation without any agreement)
This process is repeated in a turn taking clock-wise fashion until reaching an agreement or reaching the deadline. To reach an agreement, all parties should accept the offer. If at the deadline no agreement has been reached, the negotiation fails.
Assume that there are three parties negotiating. The first party makes an offer (Offer A).
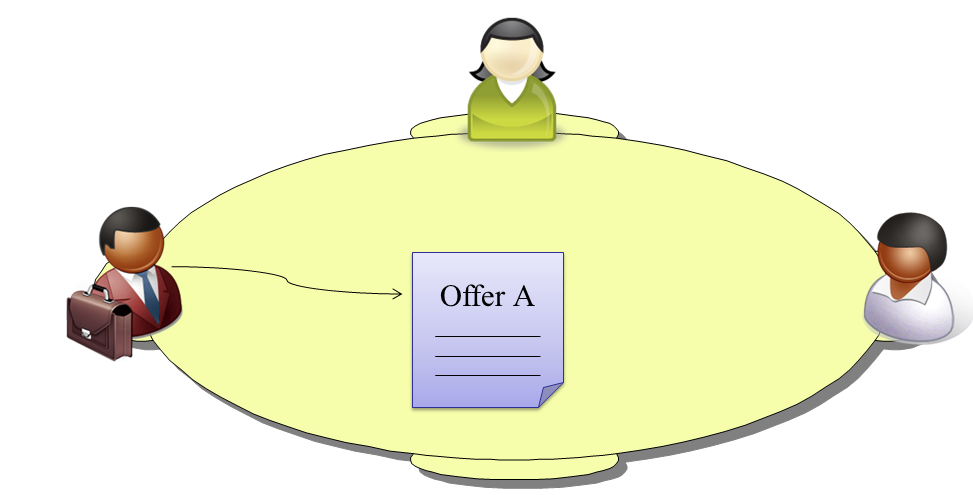
The second party can accept this offer or make a counter offer or walk way. Let assume that she decides to make a counter offer (Offer B).
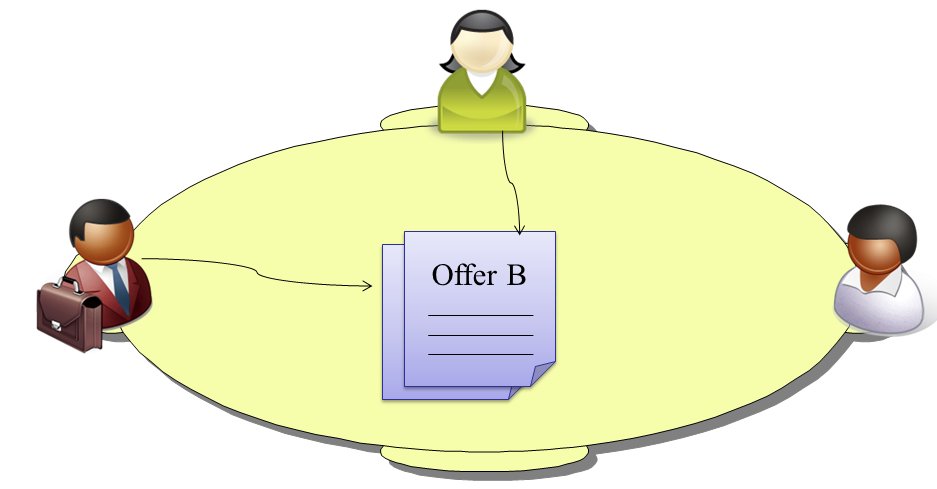
Assume that third party and the first party accept the current offer on the negotiation table. Since they all agree on this offer (i.e. Offer B made by the second party), the negotiation ends with this offer.
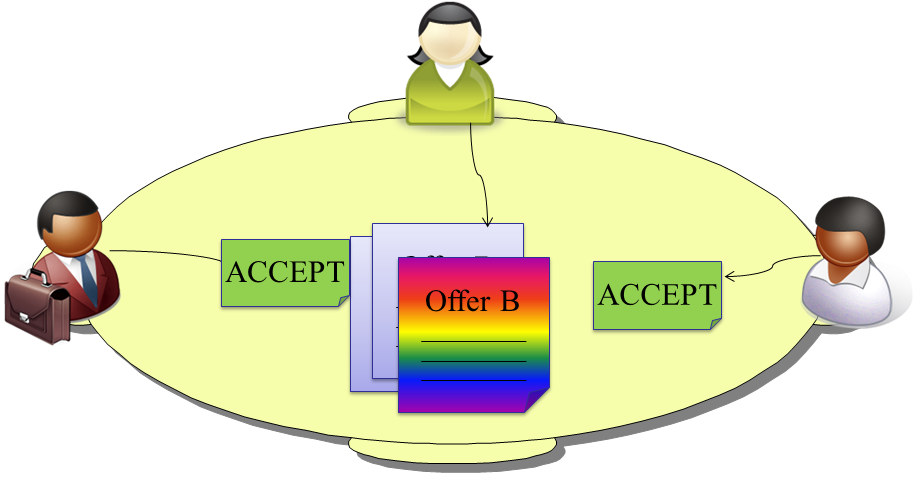
The agent always evaluate the last offer made during the negotiation and the first party always start with an offer. An example is given below:
Round: 1
-
Party 1 makes an offer; lets say
c1. -
Party 2 can accept this offer or make a counter offer. Lets make a counter offer
c2. -
Party 3 can accept
c2or makes a counter offer. Lets say it accepts this offer.
Round 2:
-
Party 1 can accept the
c2or make a counter offer. Lets say accept then the negotiation ends withc2.
Please create an issue, if you find any errors or you want a topic covered in this wiki.
- Java Programming Cheatsheet
- Setting Up Genius Environment
- Stacked Alternating Offers Protocol
- AbstractNegotationParty Methods
- How to generate a random bid?
- How to generate a random bid with a utility threshold?
- How to change the content of a bid?
- How to keep track of time in a negotiation session?
- How to get the maximum and minimum bid?
- How to iterate all bids in a domain?
- How to access weights of each issue?
- How to access the evaluation of a value?