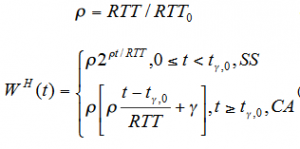Siddesh LC (16CO144) - [email protected]
Shreyas Pandith (16CO142) - [email protected]
Praveen Naik S (16Co133) - [email protected]
Validate the ns-3 implementation of TCP Hybla.
TCP Hybla is targeted to improve the performance TCP in Satellite networks where RTT is usually large. In this project, the aim is to validate ns-3 TCP Hybla implementation by comparing the results obtained from it to those obtained by simulating Linux TCP Hybla.
A key component of TCP is a congestion-control mechanism. One of the newer congestion algorithms that aims to improve network connection performance is TCP Hybla. Hybla is designed to address some of the negative effects of long network Round-Trip Times (RTT) to include reduction of the Congestion Window (cwnd) growth rate, and multiple losses in one Congestion Window. To address the issue of slow cwnd increase, TCP Hybla removes the reliance on RTT from the cwnd algorithm. This is done by adjusting the size of the cwnd to a normalized ratio of the previous window which results in a larger average cwnd as shown in the calculations below:
The TCP Hybla segment (packet) transmission rate function BH(t) was given by:
BH(t) = (WH(t) /RTT) = (1/RTT0) 2^(t/RTT0) . . . . . (SS)
BH(t) = (WH(t) /RTT) = (1/RTT0) ( (t - tγ,0)/RTT0+ γ ) . . . . (CA)
We can obtain the TCP Hybla throughput function TH(t) by integrating BH(t):
You can see that the throughput function of Hybla TCP is INDEPENDENT of RTT
To alleviate packet loss in the window, TCP Hybla uses Selective Acknowledgement (SACK) which allows the sender to know exactly which packets have been sent successfully, and the ability to send more than one packet per RTT.
Another enhancement of TCP Hybla is packet spacing during transmission. As previously stated, Hybla results in a larger cwnd size which can result in erratic transmission bursts. These bursts can be smoothed out using more intermittent transmissions and spacing each transmission out over a period of time. TCP Hybla is well suited for satellite transmissions and other connections that typically have a high RTT.
Direct Code Execution
Direct Code Execution (DCE) is a framework over ns-3 that provides a feature to run simulations using real Linux network stack. Besides, it provides a feature to use real network applications (such as iperf) inside ns-3 environment without changing their code. This feature helps to leverage the functionalities of existing network tools available for Linux inside the ns-3 environment. The main goal of the assignments listed below is to use DCE and validate the implementation of different TCPs in ns-3. All the projects listed are of direct interest to the ns-3 community.