-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.9k
User Guide
- Simple Examples For Getting Started
- Command-line Usage Information
- The Output Directory
- The Graph Database
- Importing OWASP Amass Results into Maltego
- Integrating OWASP Amass into Your Work
The amass tool and all the subcommands show options using the '-h' and '-help' flags:
amass -helpCheck the version by performing the following:
amass -versionThe most basic use of the tool for subdomain enumeration:
amass enum -d example.comTypical parameters for DNS enumeration:
$ amass enum -v -src -ip -brute -min-for-recursive 2 -d example.com
[Google] www.example.com
[VirusTotal] ns.example.com
...Executing the tool via the Docker image:
docker run -v OUTPUT_DIR_PATH:/.config/amass/ caffix/amass:latest enum --listThe volume argument allows the Amass graph database to persist between executions and output files to be accessed on the host system. The first field (left of the colon) of the volume option is the amass output directory that is external to Docker, while the second field is the path, internal to Docker, where amass will write the output files.
The amass tool has several subcommands shown below for handling your Internet exposure investigation.
| Subcommand | Description |
|---|---|
| intel | Collect open source intelligence for investigation of the target organization |
| enum | Perform DNS enumeration and network mapping of systems exposed to the Internet |
| viz | Generate visualizations of enumerations for exploratory analysis |
| track | Compare results of enumerations against common target organizations |
| db | Manage the graph databases storing the enumeration results |
Each subcommand has its own arguments that are shown in the following sections.
The intel subcommand can help you discover additional root domain names associated with the organization you are investigating. The data source sections of the configuration file are utilized by this subcommand in order to obtain passive intelligence, such as reverse whois information.
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -active | Enable active recon methods | amass intel -active -addr 192.168.2.1-64 -p 80,443,8080 |
| -addr | IPs and ranges (192.168.1.1-254) separated by commas | amass intel -addr 192.168.2.1-64 |
| -asn | ASNs separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass intel -asn 13374,14618 |
| -cidr | CIDRs separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass intel -cidr 104.154.0.0/15 |
| -config | Path to the INI configuration file | amass intel -config config.ini |
| -d | Domain names separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass intel -whois -d example.com |
| -demo | Censor output to make it suitable for demonstrations | amass intel -demo -whois -d example.com |
| -df | Path to a file providing root domain names | amass intel -whois -df domains.txt |
| -dir | Path to the directory containing the graph database | amass intel -dir PATH -cidr 104.154.0.0/15 |
| -ef | Path to a file providing data sources to exclude | amass intel -whois -ef exclude.txt -d example.com |
| -exclude | Data source names separated by commas to be excluded | amass intel -whois -exclude crtsh -d example.com |
| -if | Path to a file providing data sources to include | amass intel -whois -if include.txt -d example.com |
| -include | Data source names separated by commas to be included | amass intel -whois -include crtsh -d example.com |
| -ip | Show the IP addresses for discovered names | amass intel -ip -whois -d example.com |
| -ipv4 | Show the IPv4 addresses for discovered names | amass intel -ipv4 -whois -d example.com |
| -ipv6 | Show the IPv6 addresses for discovered names | amass intel -ipv6 -whois -d example.com |
| -list | Print the names of all available data sources | amass intel -list |
| -log | Path to the log file where errors will be written | amass intel -log amass.log -whois -d example.com |
| -max-dns-queries | Maximum number of concurrent DNS queries | amass intel -max-dns-queries 200 -whois -d example.com |
| -noresolvrate | Disable resolver rate monitoring | amass intel -cidr 104.154.0.0/15 -noresolvrate |
| -noresolvscore | Disable resolver reliability scoring | amass intel -cidr 104.154.0.0/15 -noresolvscore |
| -o | Path to the text output file | amass intel -o out.txt -whois -d example.com |
| -org | Search string provided against AS description information | amass intel -org Facebook |
| -p | Ports separated by commas (default: 443) | amass intel -cidr 104.154.0.0/15 -p 443,8080 |
| -r | IP addresses of preferred DNS resolvers (can be used multiple times) | amass intel -r 8.8.8.8,1.1.1.1 -whois -d example.com |
| -rf | Path to a file providing preferred DNS resolvers | amass intel -rf data/resolvers.txt -whois -d example.com |
| -src | Print data sources for the discovered names | amass intel -src -whois -d example.com |
| -timeout | Number of minutes to execute the enumeration | amass intel -timeout 30 -d example.com |
| -whois | All discovered domains are run through reverse whois | amass intel -whois -d example.com |
This subcommand will perform DNS enumeration and network mapping while populating the selected graph database. All the setting available in the configuration file are relevant to this subcommand. The following flags are available for configuration:
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -active | Enable active recon methods | amass enum -active -d example.com -p 80,443,8080 |
| -aw | Path to a different wordlist file for alterations | amass enum -aw PATH -d example.com |
| -bl | Blacklist of subdomain names that will not be investigated | amass enum -bl blah.example.com -d example.com |
| -blf | Path to a file providing blacklisted subdomains | amass enum -blf data/blacklist.txt -d example.com |
| -brute | Perform brute force subdomain enumeration | amass enum -brute -d example.com |
| -config | Path to the INI configuration file | amass enum -config config.ini |
| -d | Domain names separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass enum -d example.com |
| -demo | Censor output to make it suitable for demonstrations | amass enum -demo -d example.com |
| -df | Path to a file providing root domain names | amass enum -df domains.txt |
| -dir | Path to the directory containing the graph database | amass enum -dir PATH -d example.com |
| -do | Path to data operations output file | amass enum -do data.json -d example.com |
| -ef | Path to a file providing data sources to exclude | amass enum -ef exclude.txt -d example.com |
| -exclude | Data source names separated by commas to be excluded | amass enum -exclude crtsh -d example.com |
| -if | Path to a file providing data sources to include | amass enum -if include.txt -d example.com |
| -include | Data source names separated by commas to be included | amass enum -include crtsh -d example.com |
| -include-unresolvable | Output DNS names that did not resolve | amass enum -include-unresolvable -d example.com |
| -ip | Show the IP addresses for discovered names | amass enum -ip -d example.com |
| -ipv4 | Show the IPv4 addresses for discovered names | amass enum -ipv4 -d example.com |
| -ipv6 | Show the IPv6 addresses for discovered names | amass enum -ipv6 -d example.com |
| -json | Path to the JSON output file | amass enum -json out.json -d example.com |
| -list | Print the names of all available data sources | amass enum -list |
| -log | Path to the log file where errors will be written | amass enum -log amass.log -d example.com |
| -max-dns-queries | Maximum number of concurrent DNS queries | amass enum -max-dns-queries 200 -d example.com |
| -min-for-recursive | Subdomain labels seen before recursive brute forcing (Default: 1) | amass enum -brute -min-for-recursive 3 -d example.com |
| -nf | Path to a file providing already known subdomain names (from other tools/sources) | amass enum -nf names.txt -d example.com |
| -noalts | Disable generation of altered names | amass enum -noalts -d example.com |
| -norecursive | Turn off recursive brute forcing | amass enum -brute -norecursive -d example.com |
| -noresolvrate | Disable resolver rate monitoring | amass enum -d example.com -noresolvrate |
| -noresolvscore | Disable resolver reliability scoring | amass enum -d example.com -noresolvscore |
| -o | Path to the text output file | amass enum -o out.txt -d example.com |
| -oA | Path prefix used for naming all output files | amass enum -oA amass_scan -d example.com |
| -passive | A purely passive mode of execution | amass enum --passive -d example.com |
| -p | Ports separated by commas (default: 443) | amass enum -d example.com -p 443,8080 |
| -r | IP addresses of preferred DNS resolvers (can be used multiple times) | amass enum -r 8.8.8.8,1.1.1.1 -d example.com |
| -rf | Path to a file providing preferred DNS resolvers | amass enum -rf data/resolvers.txt -d example.com |
| -src | Print data sources for the discovered names | amass enum -src -d example.com |
| -timeout | Number of minutes to execute the enumeration | amass enum -timeout 30 -d example.com |
| -w | Path to a different wordlist file | amass enum -brute -w wordlist.txt -d example.com |
Create enlightening network graph visualizations that add structure to the information gathered. This subcommand only leverages the 'output_directory' and remote graph database settings from the configuration file.
The files generated for visualization are created in the current working directory and named amass_TYPE
Switches for outputting the DNS and infrastructure findings as a network graph:
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -config | Path to the INI configuration file | amass viz -config config.ini -d3 |
| -d | Domain names separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass viz -d3 -d example.com |
| -d3 | Output a D3.js v4 force simulation HTML file | amass viz -d3 -d example.com |
| -df | Path to a file providing root domain names | amass viz -d3 -df domains.txt |
| -dir | Path to the directory containing the graph database | amass viz -d3 -dir PATH -d example.com |
| -enum | Identify an enumeration via an index from the db listing | amass viz -enum 1 -d3 -d example.com |
| -gexf | Output to Graph Exchange XML Format (GEXF) | amass viz -gephi -d example.com |
| -graphistry | Output Graphistry JSON | amass viz -graphistry -d example.com |
| -i | Path to the Amass data operations JSON input file | amass viz -d3 -d example.com |
| -maltego | Output a Maltego Graph Table CSV file | amass viz -maltego -d example.com |
| -visjs | Output HTML that employs VisJS | amass viz -visjs -d example.com |
Shows differences between enumerations that included the same target(s) for monitoring a target's attack surface. This subcommand only leverages the 'output_directory' and remote graph database settings from the configuration file. Flags for performing Internet exposure monitoring across the enumerations in the graph database:
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -config | Path to the INI configuration file | amass track -config config.ini |
| -d | Domain names separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass track -d example.com |
| -df | Path to a file providing root domain names | amass track -df domains.txt |
| -dir | Path to the directory containing the graph database | amass track -dir PATH |
| -history | Show the difference between all enumeration pairs | amass track -history |
| -last | The number of recent enumerations to include in the tracking | amass track -last NUM |
| -since | Exclude all enumerations before a specified date (format: 01/02 15:04:05 2006 MST) | amass track -since DATE |
Performs viewing and manipulation of the graph database. This subcommand only leverages the 'output_directory' and remote graph database settings from the configuration file. Flags for interacting with the enumeration findings in the graph database include:
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -config | Path to the INI configuration file | amass db -config config.ini |
| -d | Domain names separated by commas (can be used multiple times) | amass db -d example.com |
| -demo | Censor output to make it suitable for demonstrations | amass db -demo -d example.com |
| -df | Path to a file providing root domain names | amass db -df domains.txt |
| -dir | Path to the directory containing the graph database | amass db -dir PATH |
| -enum | Identify an enumeration via an index from the listing | amass db -enum 1 -show |
| -import | Import an Amass data operations JSON file to the graph database | amass db -import PATH |
| -ip | Show the IP addresses for discovered names | amass db -show -ip -d example.com |
| -ipv4 | Show the IPv4 addresses for discovered names | amass db -show -ipv4 -d example.com |
| -ipv6 | Show the IPv6 addresses for discovered names | amass db -show -ipv6 -d example.com |
| -list | Print enumerations in the database and filter on domains specified | amass db -list |
| -show | Print the results for the enumeration index + domains provided | amass db -show |
| -src | Print data sources for the discovered names | amass db -show -src -d example.com |
Amass has several files that it outputs during an enumeration (e.g. the log file). If you are not using a database server to store the network graph information, then Amass creates a file based graph database in the output directory. These files are used again during future enumerations, and when leveraging features like tracking and visualization.
By default, the output directory is created in the operating system default root directory to use for user-specific configuration data and named amass. If this is not suitable for your needs, then the subcommands can be instructed to create the output directory in an alternative location using the '-dir' flag.
If you decide to use an Amass configuration file, it will be automatically discovered when put in the output directory and named config.ini.
All Amass enumeration findings are stored in a graph database. This database is either located in a single file within the output directory or connected to remotely using settings provided by the configuration file.
When a new enumeration begins and a graph database already exists with previous findings for the same target(s), the subdomain names from those previous enumerations are utilized in the new enumeration. New DNS queries are performed against those subdomain names to ensure that they are still legitimate and to obtain current IP addresses.
The results from each enumeration is stored separately in the graph database, which allows the tracking subcommand to look for differences across the enumerations and provide the user with highlights about the target.
There is nothing preventing multiple users from sharing a single (remote) graph database and leveraging each others findings across enumerations.
The GraphDB is storing all the domains that were found for a given enumeration. It stores the associated information such as the ip, ns_record, a_record, cname, ip block and associated source for each one of them as well. Each enumeration is identified by a uuid.
Here is an example of graph for an enumeration run on example.com:
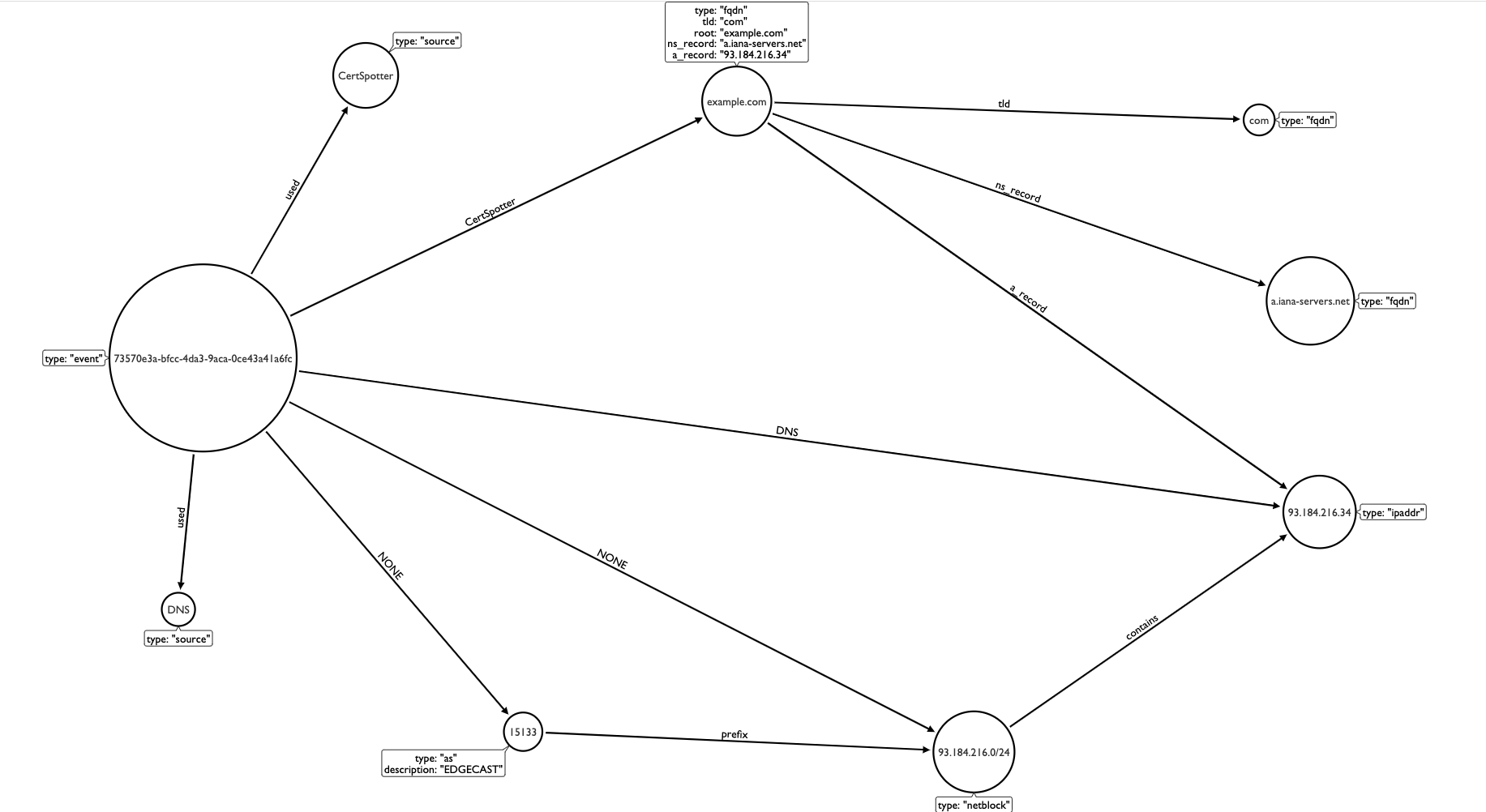
- Convert the Amass data into a Maltego graph table CSV file:
amass viz -maltego- Import the CSV file with the correct Connectivity Table settings:
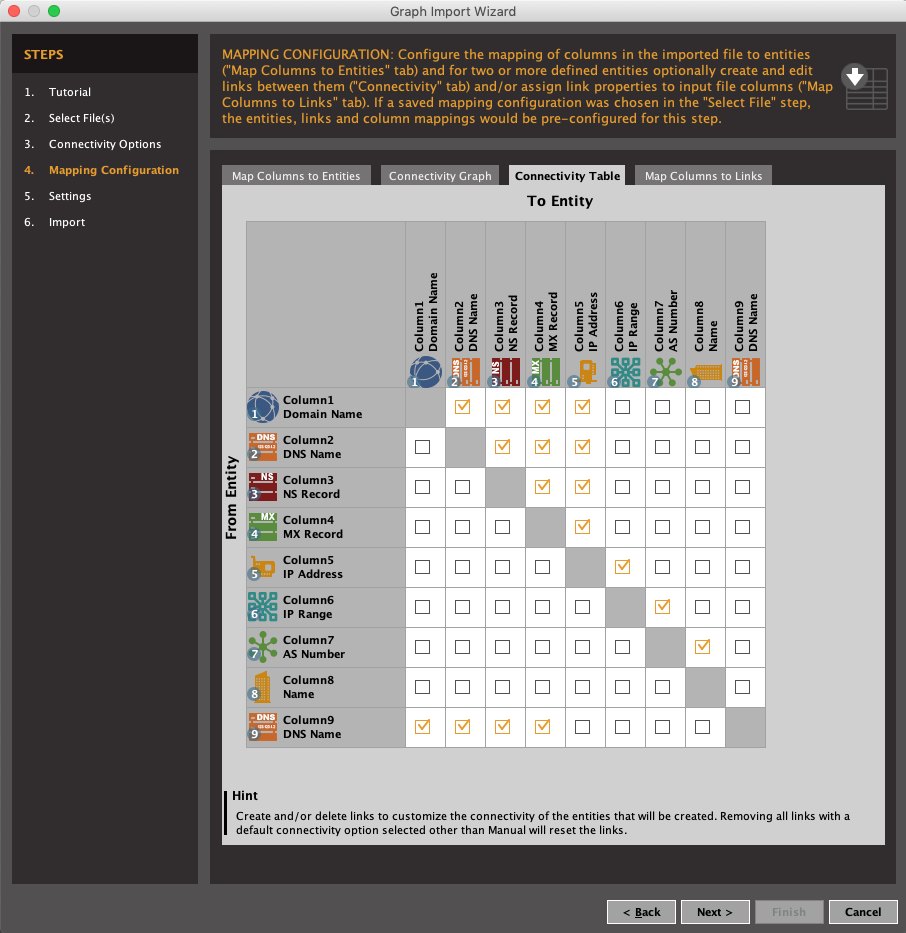
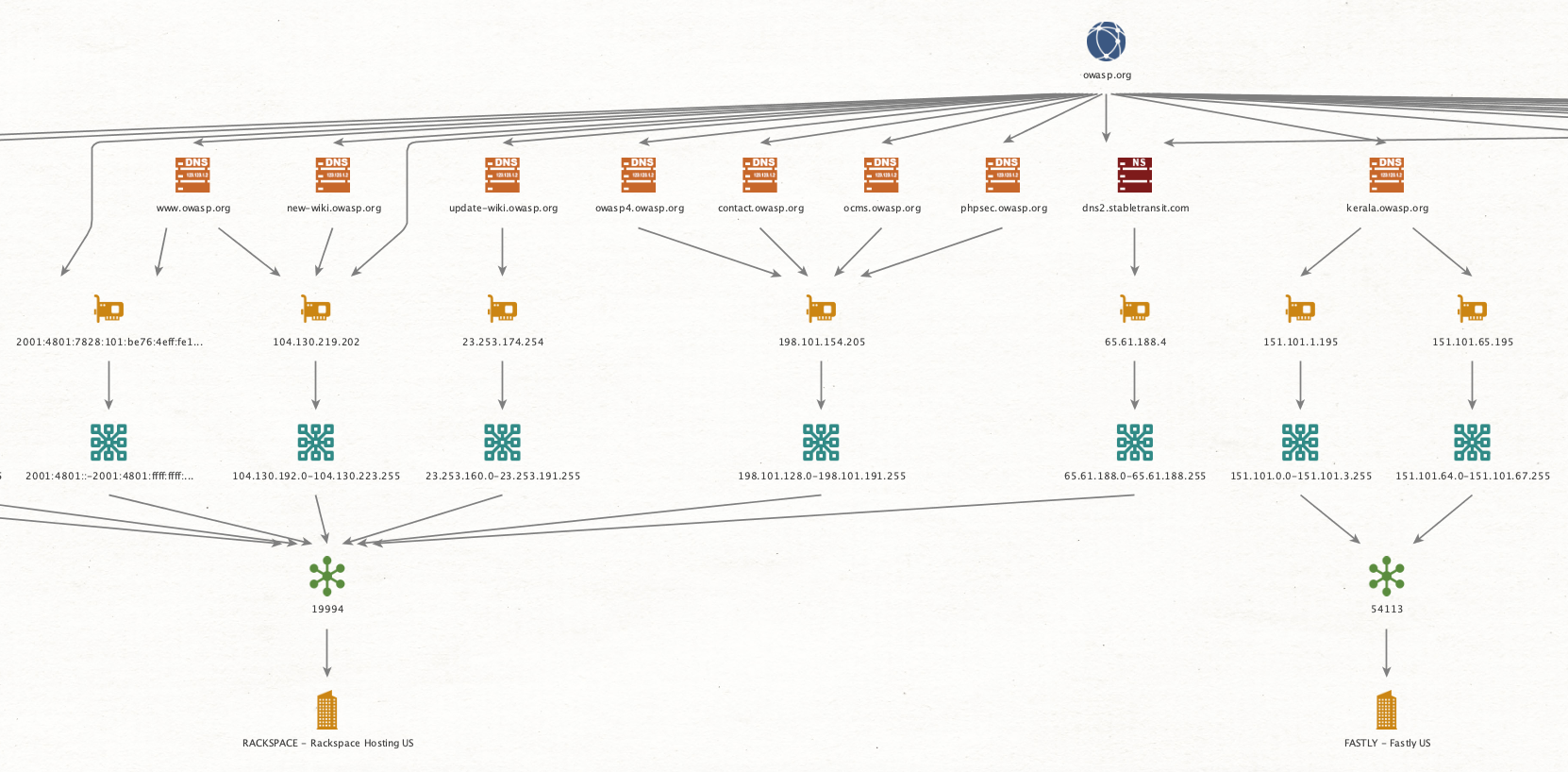
- All the Amass findings will be brought into your Maltego Graph:
If you are using the amass package within your own Go code, be sure to properly seed the default pseudo-random number generator:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
"github.com/OWASP/Amass/v3/config"
"github.com/OWASP/Amass/v3/datasrcs"
"github.com/OWASP/Amass/v3/enum"
"github.com/OWASP/Amass/v3/systems"
)
func main() {
// Seed the default pseudo-random number generator
rand.Seed(time.Now().UTC().UnixNano())
sys, err := systems.NewLocalSystem(config.NewConfig())
if err != nil {
return
}
sys.SetDataSources(datasrcs.GetAllSources(sys))
e := enum.NewEnumeration(sys)
if e == nil {
return
}
defer e.Close()
// Setup the most basic amass configuration
e.Config.AddDomain("example.com")
e.Start()
for _, o := range e.ExtractOutput(nil) {
fmt.Println(o.Name)
}
}In case you get an error saying "Failed to create the graph", try changing the output directory in the config:
cfg := config.NewConfig()
cfg.Dir = "/tmp"
sys, err := services.NewLocalSystem(cfg)