Large frontend codebase is difficult to manage. We can separate frontend code into UI Layer and BL Layer.
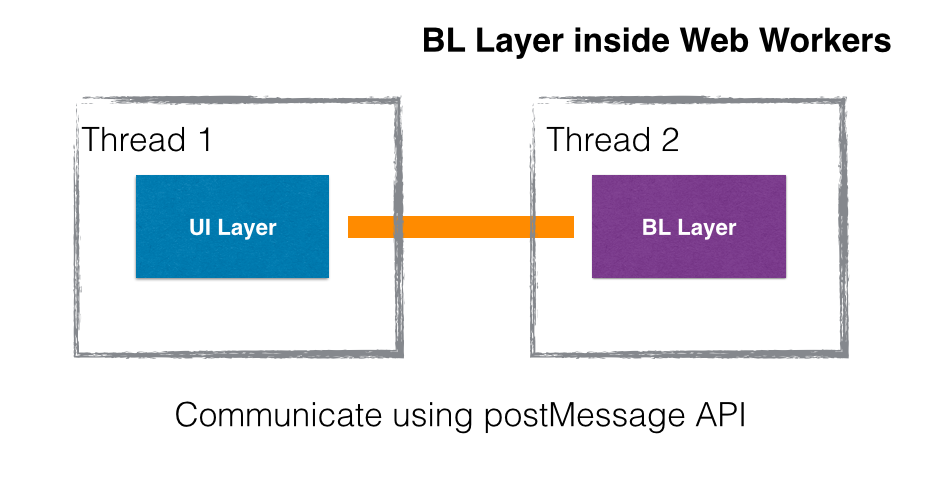
I have wrote a blog on this topic - https://medium.com/@nsisodiya/flux-inside-web-workers-cc51fb463882, Business Layer (BL) layer can be executed inside Web workers.
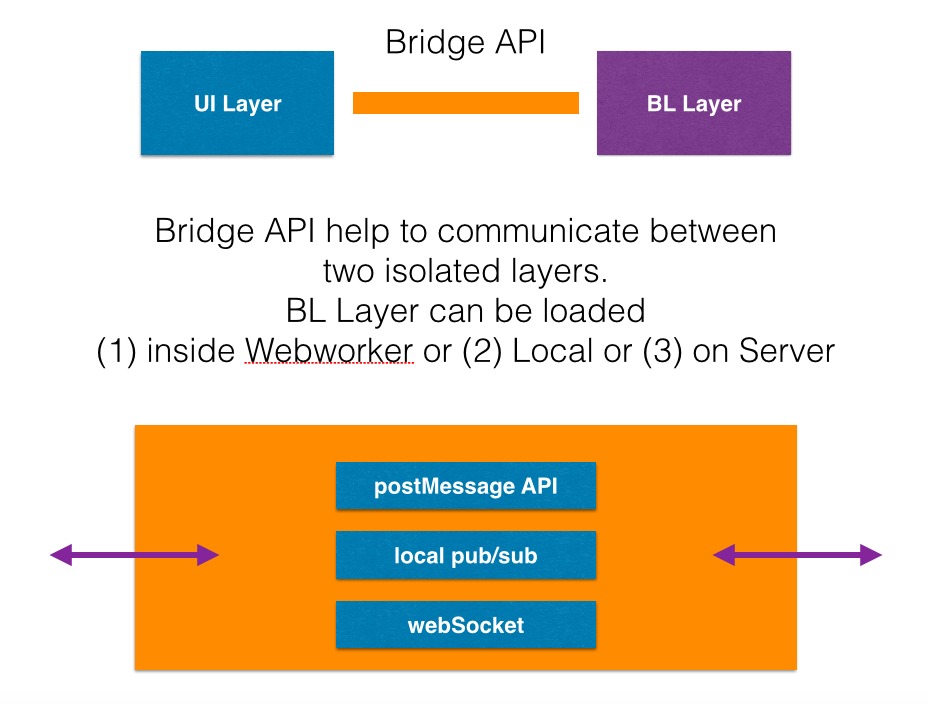
Both Layer can communicate with each other using postMessage API.
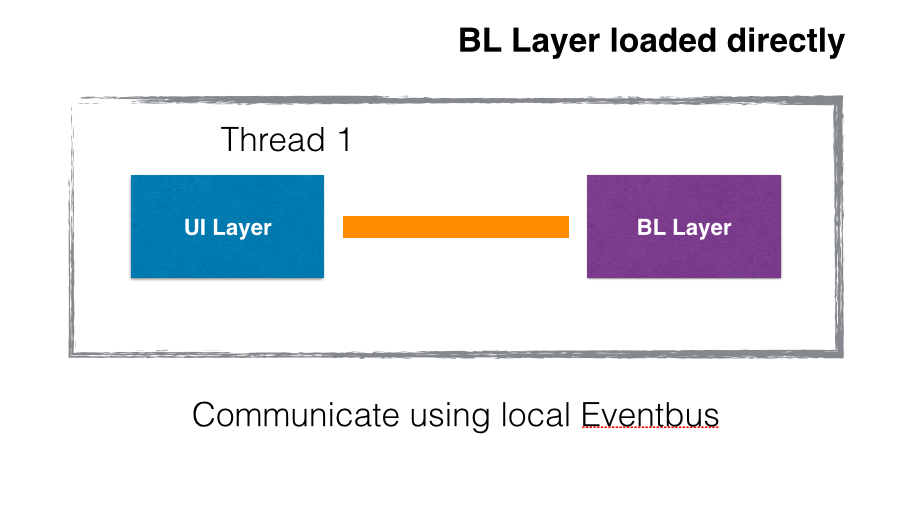
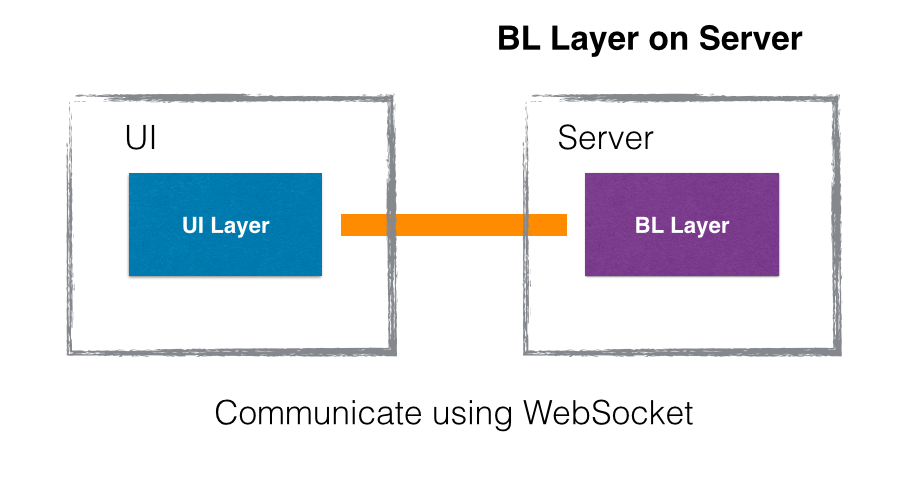
Loading BL Layer (Flux) inside Web Workers is good, but what about the browsers who do have support of Web workers. In such cases, BL Layer can be loaded on UI thread itself along with UI Layer. Both can communicate using a "shared event bus or message broker". Lets have a 3rd case, when BL Layer is executing on server. Then Both Layer can communicate using WebSocket.
So we now have 3 methods of communication.
"Bridge API" is a wrapper over all 3 methods.
"Bridge API" is basically a communication wrapper between two isolated code. One JavaScript Code can communicate to another JavaScript Code running in same or different environment. This isolated code can present anywhere. An Application can have multiple Bridge.
Bridge is created mainly for UI-BL Layer communication, but It can be useful in many places.
- Worker - done
- Local - done
- WebSocket - TODO
UI-BL Layer Bridge
UI Layer <-------------> BL Layer
- Bridge will use == "Websocket" when BL is executing on Server
- Bridge will use == "postMessage API" when BL is executing inside WebWorker
- Bridge will use == "internal pubsub" when BL is executing directly on UI Thread.
npm install bl-layer-loader
var BLLayerLoader = require('bl-layer-loader');
var bridge = BLLayerLoader.load({
url: 'http://cdnserver.com/dist/worker.bundle.js',
method: "Local"
});
var bridge = BLLayerLoader.load({
url: './dist/worker.bundle.js',
method: "Local"
});
var bridge = BLLayerLoader.load({
url: 'http://cdnserver.com/dist/worker.bundle.js',
method: "Worker"
});
//or
var bridge = BLLayerLoader.load({
url: 'ws://apiserver.com/app',
method: "WebSocket"
});UI Layer call BLLayerLoader.load method to load BLLayer. It return bridge variable which will be used in UI Layer. BL Layer also need bridge variable. In order to get bridge variable, you need use .getBLBridge method.
//ON BL Layer
var bridge = BLLayerLoader.getBLBridge();Because we need to load remote script, we cannot use bridge in sync way. isBridgeReady is a parameter which can check that bridge is ready to use or not.
bridge.isBridgeReady // boolean - true/falseIt accept callback and fire when bridge is ready, if bridge is already ready then it fire immediately
bridge.onReady(callback)if bridge is not ready, you can subscribe but you cannot publish anything. bridge may or may not hold messages in queue. [To be decided]
bridge.on(path, callback) it accept callback, whenever any message comes, it will be fired.
"*" means, get all messages !
on method is used to subscribe events. Please note that this is not equivalent to EventBus. In EventBus, you can publish or subscribe events. but In bridge we have two ends. Message published at one end will be delivered to other end.
BL Layer may subscribe to some events with some callbacks but your BL layer cannot publish those event, It is UI Layer who will publish those events.
Similarly UI Layer may subscribe to some events with some callback but your UI layer cannot publish those events, It is the BL Layer who will publish those events.
var id = bridge.on("*", function(payload, sendBack){
var newData = process(payload);
sendBack(newData);
});id will be used to unsubscribe.
.post term is derived from .postMessage
bridge.post(path, payload)
//OR
bridge.post(path, payload, callback)- path is like /actions/Store/etc, string
- payload is any object
- callback - [Optional] executed when other layer sendBack some data.
bridge.off(id)Unsubscribe, receiving message !
//On UI Layer
bridge.post("/actions/add", {first: 3, second: 5}, function(data){
console.log("Sum is - " + data);
});//On BL Layer
var id = bridge.on("/actions/add", function(payload, sendBack){
var r = payload.first + payload.second;
sendBack(r);
});//On UI Layer
var id = bridge.on("/models/usersModel", function(payload , sendBack){
console.log("User Information got Changed - ", payload);
//sendBack is optional, sometimes we do not need to send anything to server.
});//On BL Layer
function ChangeEmail(userModel, newEmail){
userModel.email = userModel;
bridge.post("/models/usersModel", userModel);
//Third Parameter is not needed because many times other layer don't need sent anything back.
}//On UI Layer
bridge.post("/models/usersModel/get", {}, function(data){
console.log("Current User Information is - ", data);
});//On BL Layer
bridge.on("/models/usersModel/get", function(payload, sendBack){
var userModel = SomeAPI.GetUserModel();
sendBack(userModel)
});//On UI Layer
bridge.on("/message/chat", function(payload, sendBack){
console.log(payload.user + ":" + payload.text);
});
$("#sendButton").click(function(){
var text = $("input#message").val();
bridge.post("/server/message", text);
});//On BL Layer on Server
bridge.on("/server/message", function(payload, sendBack){
bridge.post("/message/chat", {
user: userInfo.userName,
text: payload
});
});bridge.on("/actions/*", function(payload, sendBack){
var newData = process(payload);
sendBack(newData);
});Master branch at https://github.com/nsisodiya/flux-inside-web-workers using this package !