An Interactive Brokers integration for Deephaven.
Interactive Brokers is a very popular brokerage in the quantitative finance world, with about $200B of customer equity. Quants and hedge funds often choose Interactive Brokers because of its low trading costs and API that facilitates automated trading. With low minimum account balances, it is also an attractive choice for individual investors.
Deephaven is the real-time query engine that is the backbone for the quantitative trading of the world's largest hedge funds, banks, and exchanges. Deephaven makes working with real-time data easy and facilitates very concise and easy-to-read code. With Deephaven, quants can create new models and get them into production quickly, traders can monitor the market and their portfolios, and managers can monitor risk.
deephaven-ib combines the low-cost trading of Interactive Brokers with the analytical power and ease of use of Deephaven Community Core to yield an open, quantitative trading platform. Basically, it provides an open platform for building quantitative trading strategies and custom analytics. You can build something simple, like a portfolio monitor, or something complex, like a fully-automated, multi-strategy quantitative hedge fund.
deephaven-ib supports trading essentially all common exchange traded products. These include:
- Stocks
- Mutual Funds
- Options
- Futures
- Futures Options
- Indexes
- Bonds
- Foreign Exchange (Forex or FX)
- Cryptocurrency
- Contracts for Differences (CFDs)
- Warrants
- Commodities
WARNING: Automated trading can go horribly wrong very quickly. Verify your code on a paper trading account before unleashing trading on an account where money can be lost. If you think this can not happen to you, read The Rise and Fall of Knight Capital. The Setup section shows configurations to prevent accidental trade submission.
For more details, see:
For help with deephaven-ib:
For Deephaven how-to guides, see:
For help with Deephaven:
- Gitter: A relaxed chat room about all things Deephaven
- Deephaven Community Slack
- Deephaven Community Core Discussions
The Deephaven query engine is built around the concept of tables, which are similar to Pandas dataframes.
Unlike Pandas dataframes, Deephaven tables can dynamically update as new data is streamed in.
As input tables change, the Deephaven query engine ensures that all queries, no matter how complex,
are kept up-to-date.
Once data is converted to a Deephaven table, it can be used in queries with any other Deephaven tables.
Data available from IB Trader Workstation (TWS) can be accessed as Deephaven tables by using deephaven-ib. As data streams in, the tables and queries using them will automatically update.
These tables include:
- General
errors: an error logrequests: requests to IB
- Contracts
contract_details: details describing contracts of interest. Automatically populated.contracts_matching: contracts matching query strings provided torequest_contracts_matching.market_rules: market rules indicating the price increment a contract can trade in. Automatically populated.short_rates: interest rates for shorting securities. Automatically populated ifdownload_short_rates=True.
- Accounts
accounts_managed: accounts managed by the TWS session login. Automatically populated.accounts_family_codes: account family. Automatically populated.accounts_groups: account groups. Automatically populated.accounts_allocation_profiles: allocation profiles for accounts. Automatically populated.accounts_value: account values. Automatically populated.accounts_overview: overview of account details. Automatically populated.accounts_summary: account summary. Automatically populated.accounts_positions: account positions. Automatically populated.accounts_pnl: account PNL. Automatically populated.
- News
news_providers: currently subscribed news sources. Automatically populated.news_bulletins: news bulletins. Automatically populated.news_articles: the content of news articles requested viarequest_news_article.news_historical: historical news headlines requested viarequest_news_historical.
- Market Data
ticks_price: real-time tick market data of price values requested viarequest_market_data.ticks_size: real-time tick market data of size values requested viarequest_market_data.ticks_string: real-time tick market data of string values requested viarequest_market_data.ticks_efp: real-time tick market data of exchange for physical (EFP) values requested viarequest_market_data.ticks_generic: real-time tick market data of generic floating point values requested viarequest_market_data.ticks_option_computation: real-time tick market data of option computations requested viarequest_market_data.ticks_trade: real-time tick market data of trade prices requested viarequest_tick_data_historicalorrequest_tick_data_realtime.ticks_bid_ask: real-time tick market data of bid and ask prices requested viarequest_tick_data_historicalorrequest_tick_data_realtime.ticks_mid_point: real-time tick market data of mid-point prices requested viarequest_tick_data_historicalorrequest_tick_data_realtime.bars_historical: historical price bars requested viarequest_bars_historical. Real-time bars change as new data arrives.bars_realtime: real-time price bars requested viarequest_bars_realtime.
- Order Management System (OMS)
orders_submitted: submitted orders FOR THE THE CLIENT'S ID. A client ID of 0 contains manually entered orders. Automatically populated.orders_status: order statuses. Automatically populated.orders_completed: completed orders. Automatically populated.orders_exec_details: order execution details. Automatically populated.orders_exec_commission_report: order execution commission report. Automatically populated.
Most tables include a ReceiveTime column. This column indicates the time the data was received by deephaven-ib. It does not represent the time the event occurred.
You may want to combine data from other sources with your IB data. Deephaven can load data from:
- CSV
- Parquet
- Kafka.
See the Deephaven Documentation for details.
Files placed in the ./docker/data/ directory are visible in the Docker container at /data/.
See Access your file system with Docker data volumes for details.
Follow these steps to run a Deephaven plus Interactive Brokers system.
Windows users need to run the commands in WSL.
To setup and configure the system:
-
Follow the Deephaven Quick Start Guide to get Deephaven running.
-
Follow the TWS Installation Instructions to get IB Trader Workstation (TWS) running.
-
Launch IB Trader Workstation (TWS).
-
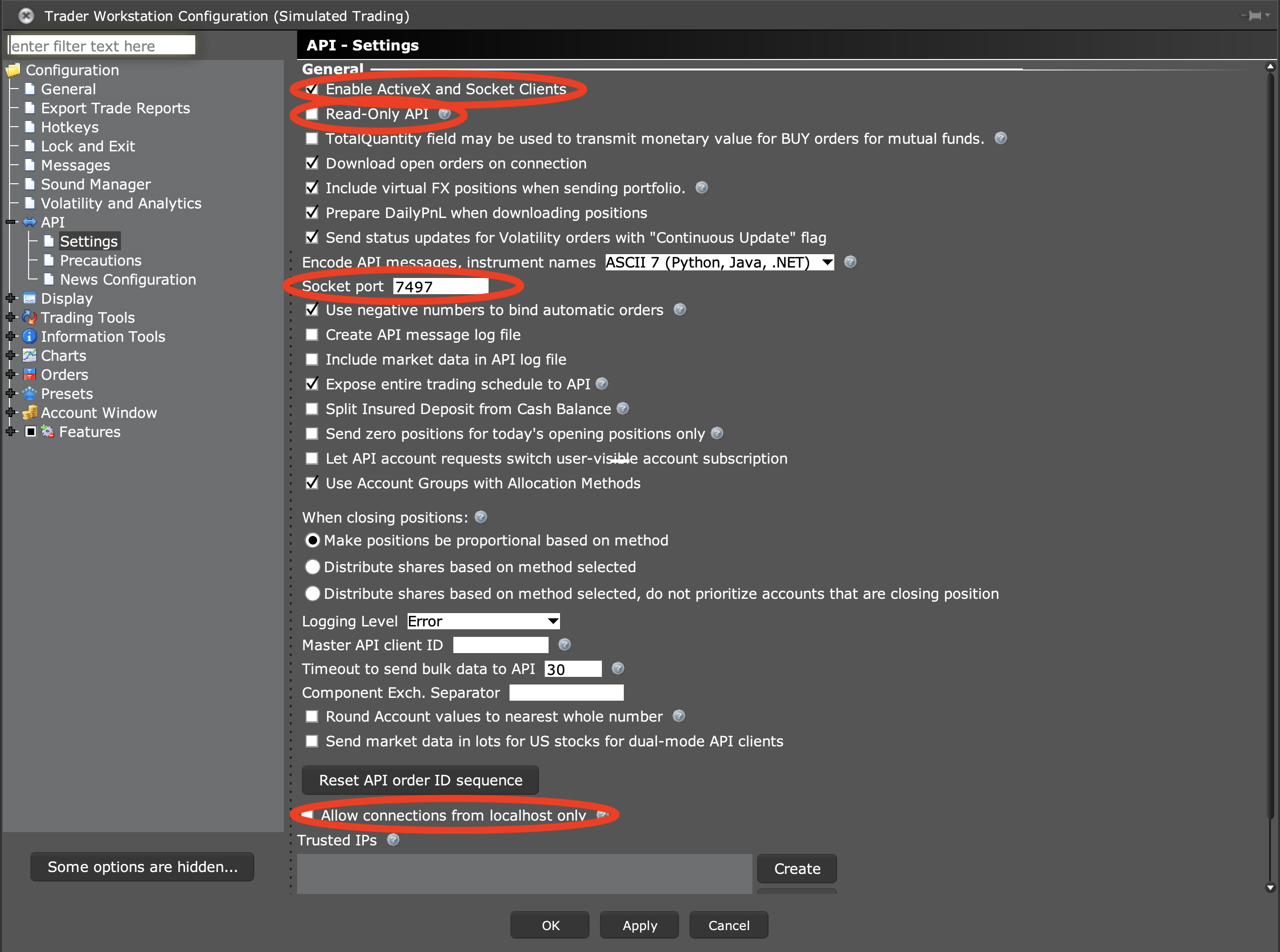
In IB Trader Workstation (TWS), click on the gear in the upper right corner.

InAPI->Settings, make sure:- "Enable ActiveX and Socket Clients" is selected.
- "Allow connections from localhost only" is not selected.
- "Read-Only API" is selected if you want to prevent trade submission from deephaven-ib.
Also, note the "Socket port" value. It is needed when connecting deephaven-ib.
-
[For Paper Trading] Log into the Interactive Brokers Web Interface.
-
[For Paper Trading] In the Interactive Brokers Web Interface, navigate to
Account->Settings->Paper Trading Accountand make sure that "Share real-time market data subscriptions with paper trading account?" is set to true. -
Once deephaven-ib is launched (see below), accept incoming connections to IB Trader Workstation (TWS). (May not be required for all sessions.)
There are multiple ways to launch Deephaven with deephaven-ib installed. The launch can either happen via a local installation or via Docker images.
For a Docker Compose example, see docker/release/.
The pip-installed Deephaven uses a lightweight Deephaven installation that is installed using pip. In this case, the pip-installed Deephaven system is installed in a Docker container.
- Create a directory for your data and scripts
mkdir data
- Create a directory for your Deephaven IDE configuration and notebooks
mkdir `pwd`/.deephaven - Launch the system:
# Set jvm_args to the desired JVM memory for Deephaven docker run -it -v data:/data -v `pwd`/.deephaven:/storage -p 10000:10000 ghcr.io/deephaven-examples/deephaven-ib python3 -i -c "from deephaven_server import Server; _server = Server(port=10000, jvm_args=['-Xmx4g','-Dauthentication.psk=DeephavenRocks!']); _server.start()"
- Launch the Deephaven IDE by navigating to http://localhost:10000/ide/ in a browser and logging in with the password
DeephavenRocks!.
The pip-installed Deephaven uses a lightweight Deephaven installation that is installed using pip. In this case,
the pip-installed Deephaven system is installed in a Docker container.
This is a good option for production scenarios where scripts need to be run and related data needs to be visualized.
- Create a directory for your data and scripts
mkdir data # your_script.py must begin with: "from deephaven_server import Server; _server = Server(port=10000, jvm_args=['-Xmx4g','-Dauthentication.psk=DeephavenRocks!']); _server.start()" # Set jvm_args to the desired JVM memory for Deephaven cp path/to/your_script.py data/your_script.py
- Create a directory for your Deephaven IDE configuration and notebooks
mkdir `pwd`/.deephaven - Launch the system:
# Set jvm_args to the desired JVM memory for Deephaven docker run -it -v data:/data -v `pwd`/.deephaven:/storage -p 10000:10000 ghcr.io/deephaven-examples/deephaven-ib python3 -i /data/your_script.py
- Launch the Deephaven IDE by navigating to http://localhost:10000/ide/ in a browser and logging in with the password
DeephavenRocks!.
The pip-installed Deephaven uses a lightweight Deephaven installation that is installed using pip. In this case, the pip-installed Deephaven system is installed directly on your local system, without Docker.
It is possible to use deephaven-ib without docker, but this is a new feature and has not been well tested. To do this:
- Install
ibapi:# pip installed version of ibapi is too old. You must download and install a more recent version. export IB_VERSION=1019.01 curl -o ./api.zip "https://interactivebrokers.github.io/downloads/twsapi_macunix.${IB_VERSION}.zip" unzip api.zip cd ./IBJts/source/pythonclient python3 setup.py install
- Install Java 11 and set the appropriate
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable. - Install deephaven-ib:
pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel pip3 install deephaven-ib
- Launch the system:
# Set jvm_args to the desired JVM memory for Deephaven # Deephaven IDE configuration and notebooks are stored to ~/.deephaven python3 -i -c "import os; from deephaven_server import Server; _server = Server(port=10000, jvm_args=['-Xmx4g','-Dauthentication.psk=DeephavenRocks!','-Dstorage.path=' + os.path.expanduser('~/.deephaven')]); _server.start()"
- Launch the Deephaven IDE by navigating to http://localhost:10000/ide/ in a browser and log in with the password
DeephavenRocks!. - Use
host="localhost"for the hostname in the examples (Windows WSL useshost="host.docker.internal", since WSL is built on Docker.)
The pip-installed Deephaven uses a lightweight Deephaven installation that is installed using pip. In this case,
the pip-installed Deephaven system is installed directly on your local system, without Docker.
This is a good option for production scenarios where scripts need to be run and related data needs to be visualized.
It is possible to use deephaven-ib without docker, but this is a new feature and has not been well tested. To do this:
- Install
ibapi:# pip installed version of ibapi is too old. You must download and install a more recent version. export IB_VERSION=1016.01 curl -o ./api.zip "https://interactivebrokers.github.io/downloads/twsapi_macunix.${IB_VERSION}.zip" unzip api.zip cd ./IBJts/source/pythonclient python3 setup.py install
- Install Java 11 and set the appropriate
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable. - Install deephaven-ib:
pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel pip3 install deephaven-ib
- Launch the system and execute a custom script:
# your_script.py must begin with: "import os; from deephaven_server import Server; _server = Server(port=10000, jvm_args=['-Xmx4g','-Dauthentication.psk=DeephavenRocks!','-Dstorage.path=' + os.path.expanduser('~/.deephaven')]); _server.start()" # Deephaven IDE configuration and notebooks are stored to ~/.deephaven # Set jvm_args to the desired JVM memory for Deephaven python3 -i your_script.py
- Launch the Deephaven IDE by navigating to http://localhost:10000/ide/ in a browser and log in with the password
DeephavenRocks!. - Use
host=localhostfor the hostname in the examples
The documentation and examples here illustrate using Deephaven's Pre-Shared Key (PSK) authentication
with the password DeephavenRocks!. Other types of Deephaven authentication can also work.
See the Deephaven Documentation for details.
Common ways to authenticate are:
To use deephaven-ib, you will need to open the Deephaven Web IDE
by navigating to http://localhost:10000/ide/ in your web browser. How you authenticate
will depend upon how authentication is configured. In the examples here, you will use the password DeephavenRocks!.
The following commands can be executed in the console.
All deephaven-ib sessions need to first create a client for interacting with IB Trader Workstation (TWS).
host is the computer to connect to. When using deephaven-ib inside
of Docker, host should be set to host.docker.internal.
port is the network port IB Trader Workstation (TWS)
communicates on. This value can be found in the IB Trader Workstation (TWS)
settings. By default, production trading uses port 7496, and paper trading uses port 7497. See Setup and TWS Initial Setup for more details.
read_only is a boolean value that is used to enable trading. By default read_only=True, preventing trading. Use read_only=False to enable trading.
is_fa is a boolean value that is used to indicate if an account is a financial advisor (FA) account or a regular acccount.
By using is_fa=True, FA account configuration details are requested. By default is_fa=False.
If is_fa=True is used on a non-FA account, everything should work fine, but there will be error messages.
If is_fa=False (the default) is used on a FA account, FA account configurations will not be populated in tables such as
accounts_groups, accounts_allocation_profiles, and accounts_aliases.
order_id_strategy is the strategy used for obtaining new order ids. Order id algorithms have tradeoffs in execution time, support for multiple, concurrent sessions, and avoidance of TWS bugs.
OrderIdStrategy.RETRY(default) - Request a new order ID from TWS every time one is needed. Retry if TWS does not respond quickly. This usually avoids a TWS bug where it does not always respond.OrderIdStrategy.BASIC- Request a new order ID from TWS every time one is needed. Does not retry, so it may deadlock if TWS does not respond.OrderIdStrategy.INCREMENT- Use the initial order ID sent by TWS and increment the value upon every request. This is fast, but it may fail for multiple, concurrent sessions connected to TWS.
For a read-write session that allows trading:
import deephaven_ib as dhib
client = dhib.IbSessionTws(host="host.docker.internal", port=7497, read_only=False)
client.connect()For a read-only session that does not allow trading:
import deephaven_ib as dhib
client = dhib.IbSessionTws(host="host.docker.internal", port=7497, read_only=True)
client.connect()For a read-only financial advisor (FA) session that does not allow trading:
import deephaven_ib as dhib
client = dhib.IbSessionTws(host="host.docker.internal", port=7497, read_only=True, is_fa=True)
client.connect()After client.connect() is called, TWS requires that the connection be accepted.
IB Trader Workstation (TWS) data is stored in the deephaven-ib client as two dictionaries of tables:
tablescontains the tables most users will want.tables_rawcontains raw IB Trader Workstation (TWS) data.
As an example, the requests table, that contains all of the requests made to IB Trader Workstation (TWS),
can be obtained by:
requests = client.tables["requests"]To display all of the tables in the Deephaven IDE, place the tables in the global namespace. This can most easily be done by:
for k, v in client.tables.items():
globals()[k] = vSimilarly, raw tables can be viewed by:
for k, v in client.tables_raw.items():
globals()[k] = vA list of available tables can be obtained by:
print(client.tables.keys())
print(client.tables_raw.keys())In IB, financial contracts include:
- Stocks
- FX
- Cryptocurrency
- Indexes
- CFDs
- Futures
- Options
- Futures Options
- Bonds
- Mutual Funds
- Warrants
- Commodities
To create a contract for use in deephaven-ib,
the contract must first be created as an ibapi.contract.Contract. Once the contract is created,
it must be registered with deephaven-ib before it
can be used.
Details on creating contracts can be found at https://interactivebrokers.github.io/tws-api/basic_contracts.html.
Registering the contract causes the contract details to appear in the contracts_details table.
from ibapi.contract import Contract
c = Contract()
c.symbol = 'AAPL'
c.secType = 'STK'
c.exchange = 'SMART'
c.currency = 'USD'
rc = client.get_registered_contract(c)
print(rc)./examples/example_all_functionality.py illustrates the creation and registration of many different types of contracts.
Market data can be requested from the client using:
request_market_datarequest_bars_historicalrequest_bars_realtimerequest_tick_data_realtimerequest_tick_data_historical
from ibapi.contract import Contract
import deephaven_ib as dhib
# Use delayed market data if you do not have access to real-time
# client.set_market_data_type(dhib.MarketDataType.DELAYED)
client.set_market_data_type(dhib.MarketDataType.REAL_TIME)
c = Contract()
c.symbol = 'AAPL'
c.secType = 'STK'
c.exchange = 'SMART'
c.currency = 'USD'
rc = client.get_registered_contract(c)
print(rc)
client.request_market_data(rc)
client.request_tick_data_realtime(rc, dhib.TickDataType.BID_ASK)
client.request_tick_data_realtime(rc, dhib.TickDataType.LAST)
client.request_tick_data_realtime(rc, dhib.TickDataType.MIDPOINT)./examples/example_all_functionality.py illustrates requesting many kinds of market data.
Market data can be requested from the client using:
request_news_historicalrequest_news_article
from ibapi.contract import Contract
from deephaven.time import to_datetime
contract = Contract()
contract.symbol = "GOOG"
contract.secType = "STK"
contract.currency = "USD"
contract.exchange = "SMART"
rc = client.get_registered_contract(contract)
print(contract)
start = "2021-01-01T00:00:00 ET"
end = "2021-01-10T00:00:00 ET"
client.request_news_historical(rc, start=start, end=end)
client.request_news_article(provider_code="BRFUPDN", article_id="BRFUPDN$107d53ea")./examples/example_all_functionality.py illustrates requesting news data.
Standard account details are requested by default. IB Trader Workstation (TWS) does not provide an API for requesting all model codes, so deephaven-ib can not subscribe to data for different model codes. If you need details on non-standard account / model code combinations, you can use:
request_account_pnlrequest_account_overviewrequest_account_positions
Orders can be created and canceled using:
order_placeorder_cancelorder_cancel_all
To place an order, register a contract with deephaven-ib,
and create an ibapi.order.Order containing details for the order.
Details on creating orders can be found at https://interactivebrokers.github.io/tws-api/orders.html.
from ibapi.contract import Contract
from ibapi.order import Order
contract = Contract()
contract.symbol = "GOOG"
contract.secType = "STK"
contract.currency = "USD"
contract.exchange = "SMART"
rc = client.get_registered_contract(contract)
print(contract)
order = Order()
order.account = "DF4943843"
order.action = "BUY"
order.orderType = "LIMIT"
order.totalQuantity = 1
order.lmtPrice = 3000
order.eTradeOnly = False
order.firmQuoteOnly = False
req = client.order_place(rc, order)
req.cancel()
client.order_place(rc, order)
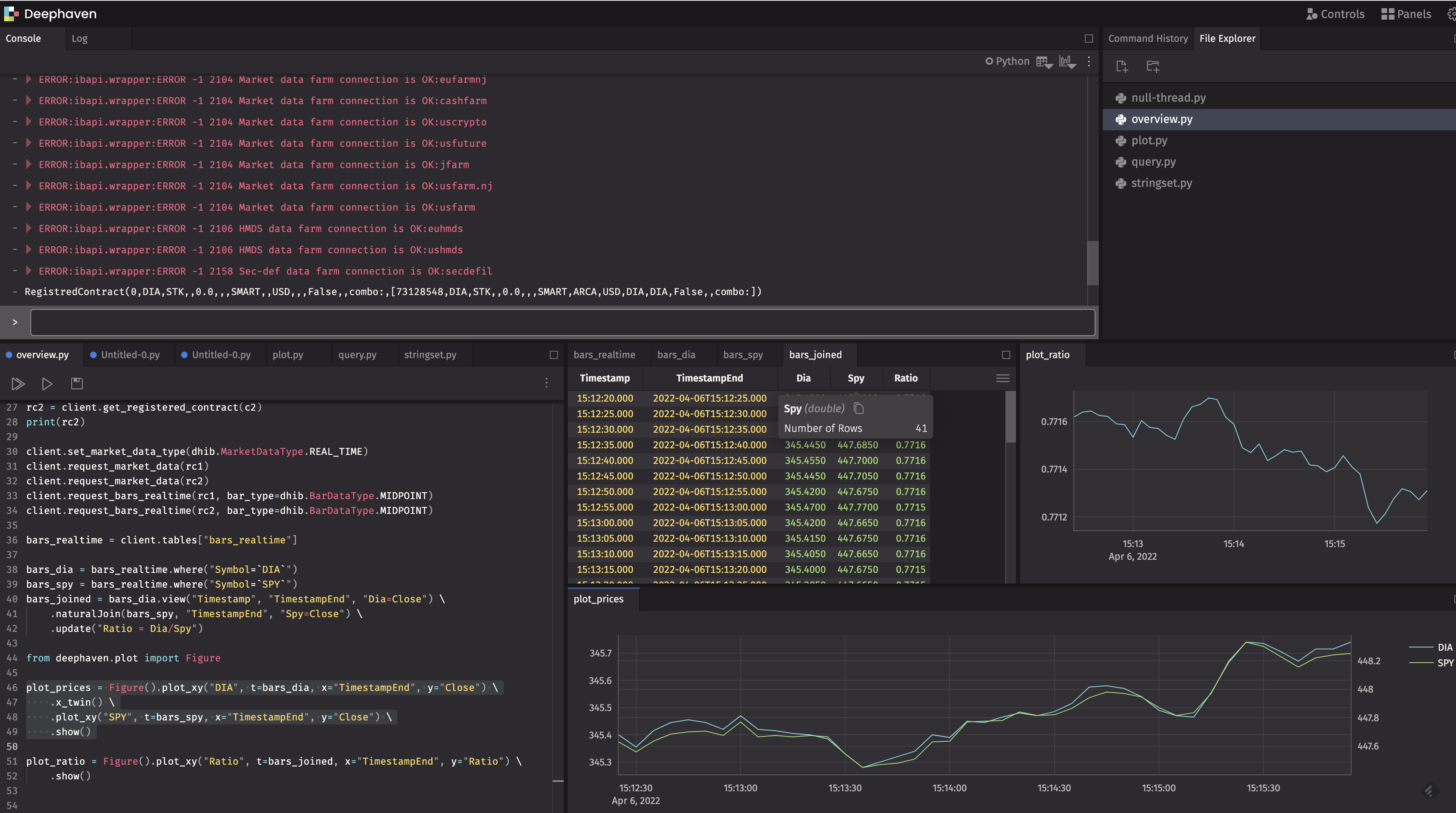
client.order_cancel_all()Deephaven has very powerful query engine that allows mathematics and queries to be applied to static and real-time data. The queries can be as simple as filtering data and as complex as artificial intelligence.
The example below computes the real-time price ratio of DIA (Dow Jones Index) and SPY (S&P 500 Index)
every 5 seconds.
For more details, see the Deephaven Coummunity Core Documentation.
from ibapi.contract import Contract
c1 = Contract()
c1.symbol = 'DIA'
c1.secType = 'STK'
c1.exchange = 'SMART'
c1.currency = 'USD'
rc1 = client.get_registered_contract(c1)
print(rc1)
c2 = Contract()
c2.symbol = 'SPY'
c2.secType = 'STK'
c2.exchange = 'SMART'
c2.currency = 'USD'
rc2 = client.get_registered_contract(c2)
print(rc2)
client.set_market_data_type(dhib.MarketDataType.REAL_TIME)
client.request_market_data(rc1)
client.request_market_data(rc2)
client.request_bars_realtime(rc1, bar_type=dhib.BarDataType.MIDPOINT)
client.request_bars_realtime(rc2, bar_type=dhib.BarDataType.MIDPOINT)
bars_realtime = client.tables["bars_realtime"]
bars_dia = bars_realtime.where("Symbol=`DIA`")
bars_spy = bars_realtime.where("Symbol=`SPY`")
bars_joined = bars_dia.view(["Timestamp", "TimestampEnd", "Dia=Close"]) \
.natural_join(bars_spy, on="TimestampEnd", joins="Spy=Close") \
.update("Ratio = Dia/Spy")Deephaven has very powerful plotting functionality for both static and real-time data.
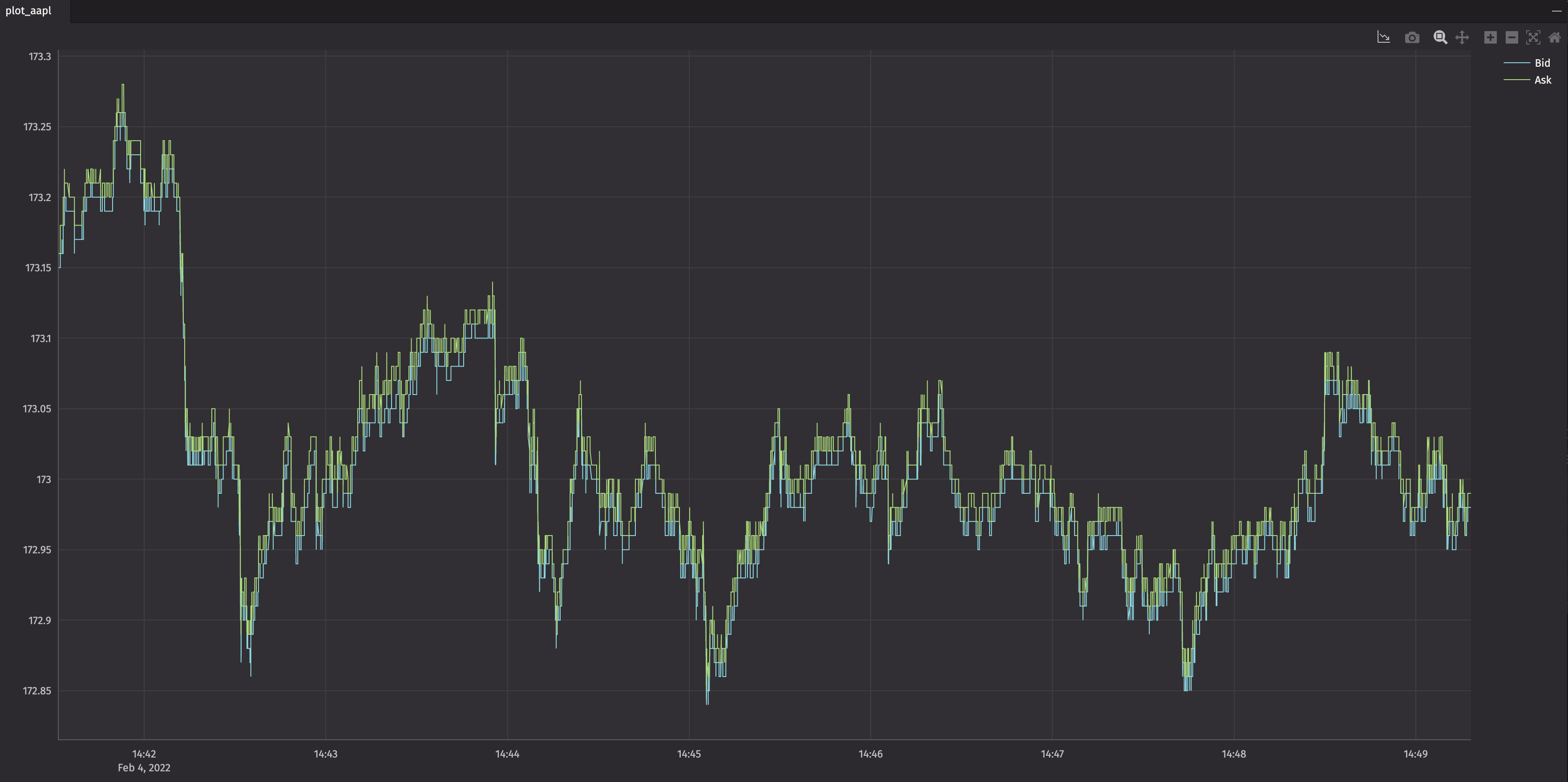
The example below plots the bid and ask prices of AAPL for every tick in the market.
For more details, see the Deephaven Coummunity Core Documentation.
from ibapi.contract import Contract
c = Contract()
c.symbol = 'AAPL'
c.secType = 'STK'
c.exchange = 'SMART'
c.currency = 'USD'
rc = client.get_registered_contract(c)
print(rc)
client.set_market_data_type(dhib.MarketDataType.REAL_TIME)
client.request_market_data(rc)
client.request_tick_data_realtime(rc, dhib.TickDataType.BID_ASK)
ticks_bid_ask = client.tables["ticks_bid_ask"]
from deephaven.plot import Figure
plot_aapl = Figure().plot_xy("Bid", t=ticks_bid_ask, x="ReceiveTime", y="BidPrice") \
.plot_xy("Ask", t=ticks_bid_ask, x="ReceiveTime", y="AskPrice") \
.show()deephaven-ib logs all IB Trader Workstation (TWS)
errors to the errors table. This table should be monitored when using deephaven-ib.
errors = client.tables["errors"]deephaven-ib and ibapi both use Python's
logging framework. By default, ERROR and higher
levels are logged. More or less logging can be displayed by changing the logging level.
To see fewer log messages:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.CRITICAL)To see all log messages:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)A discussion of available logging levels can be found in the Python logging module documentation.
If you can not solve your problems through either the errors table or through logging, you can try:
- deephaven-ib API Documentation
- Interactive Brokers Support
- Gitter: A relaxed chat room about all things Deephaven
- Deephaven Community Slack
You may encounter an error that looks like: Takes N positional arguments but M were given. If you see a problem like this, your ibapi version does not match the version needed by deephaven-ib. The ibapi version in PyPI is ancient and appears to have been abandoned by Interactive Brokers. Currently Interactive Brokers is delivering ibapi either via the IB Trader Workstation (TWS) download or via git.
To check your ibapi version:
import ibapi
print(ibapi.__version__)If your version is 9.x, it is the old version from PyPI. To install the required ibapi version:
# pip installed version of ibapi is too old. You must download and install a more recent version.
export IB_VERSION=1019.01
curl -o ./api.zip "https://interactivebrokers.github.io/downloads/twsapi_macunix.${IB_VERSION}.zip"
unzip api.zip
cd ./IBJts/source/pythonclient
python3 setup.py installNote that the ibapi API is very unstable. You likely need the exact version mentioned here for deephaven-ib to function. If you want a better installation experience and more flexability with the ibapi version, reach out to Interactive Brokers and let them know that you want them to start publishing the latest ibapi versions to PyPI.
Examples can be found in ./examples.