But that which will excite the greatest astonishment by far, and which indeed especially moved me to call the attention of all astronomers and philosophers, is this: namely, that I have observed four planets, neither known nor observed by any one of the astronomers before my time, which have their orbits round a certain bright star, one of those previously known, like Venus or Mercury round the sun, and are sometimes in front of it, sometimes behind it, though they never depart from it beyond certain limits. All of which facts were discovered and observed a few days ago by the help of a telescope devised by me, through God’s grace first enlightening my mind. ~ The Sidereal Messenger - Galileo Galilei [1620]
This repository contains configuration to establish a Docker container using Docker Compose to run JupyterLab with the Pyspark kernel. It includes the installation of Plotly for interactive visualisations and Spark Monitor for observing job progress inside the notebook environment.
It is based off the jupyter/pyspark-notebook:latest container, which in turn is based of the jupyter/scipy-notebook:latest container. All of the standard JupyterLab modules are included here.
- Jupyter Lab 3
- Pyspark 3
- OpenJDK JRE 11
- Plotly
- Spark Monitor
- Default
jovyanuser password [jupyter] with sudo rights for installing additional packages in the terminal - WARN logging is disabled in Pyspark to reduce messages in notebooks
- Spark throws a warning on first start for Illegal Reflection detailed here: Spark-34096
- The
.ipythonenvironment is stored inside the contain and will not persist through containerrmandup -dcycles. This is due to the inclusion ofSpark Monitor, but could be improved later.
First ensure that the following pre-requisites are installed:
If running Ubuntu, IP forwarding was required. ufw was also blocking apt initially.
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
sudo systemctl stop ufwOnce docker-compose is available in the system path, build the container:
sudo docker-compose build jupyterlab-pysparksudo docker-compose up -d jupyterlab-pyspark
Starting jupyter-pyspark ... doneAny additionally installed packages will persist if the container is stopped. The container can then be easily restarted later. Stopping the container will prevent it starting automatically on the next system reboot.
sudo docker-compose stop jupyterlab-pyspark
sudo docker-compose restart jupyterlab-pysparkRemoving the container will lose any additionally installed packages or configuration.
sudo docker-compose rm jupyterlab-pysparkJupyterLab
Once the container has started, open a browser and navigate to: localhost:8888
The default password as configured is: jupyter
Spark UI
Once a Pyspark session has been started, the Spark UI can be accessed using: localhost:4040
In order to see the Spark Monitor in a notebook, the SparkMonitor menu item Toggle Monitors needs to be enabled. The Spark UI can also be access directly in JupyterLab using the Open Spark UI menu item.
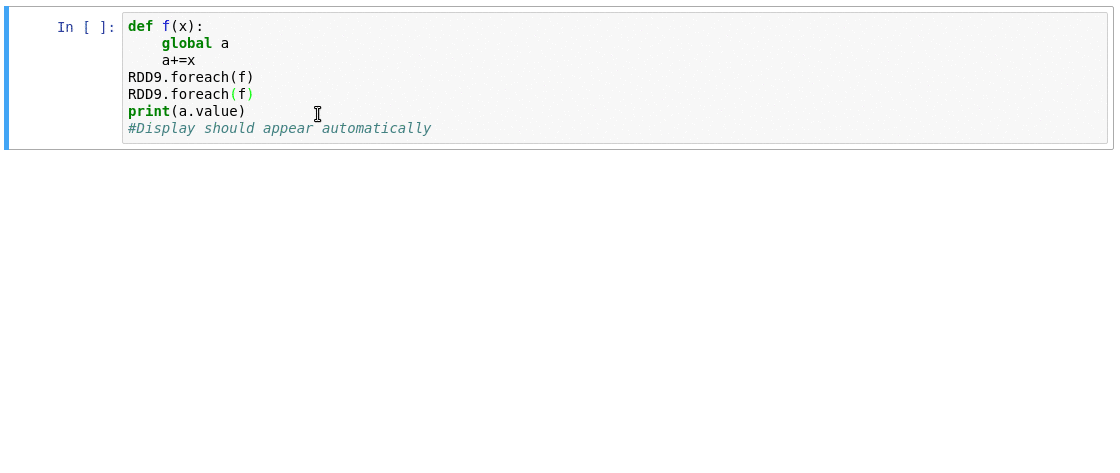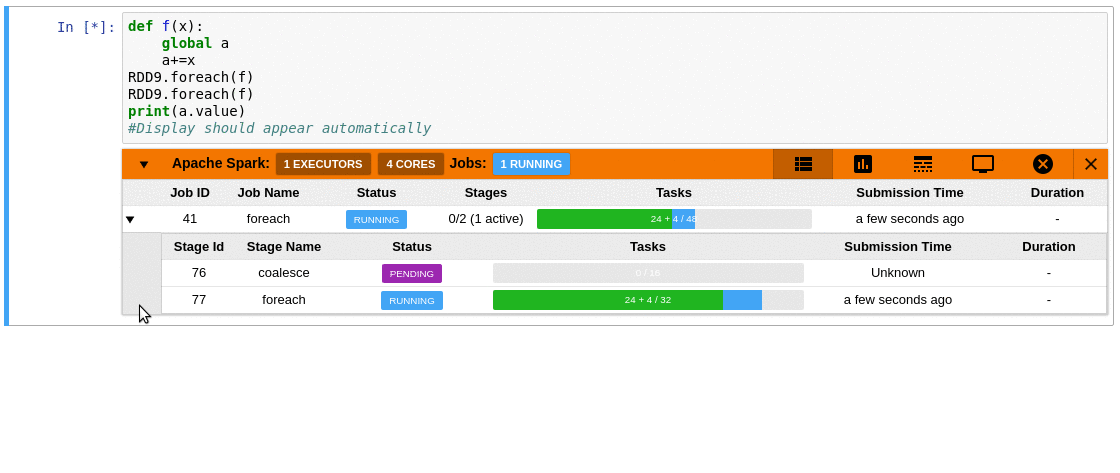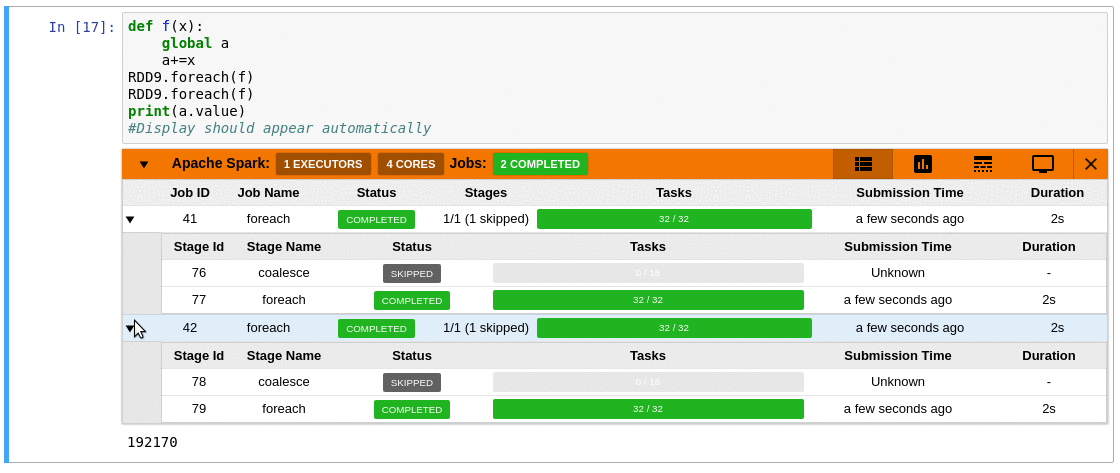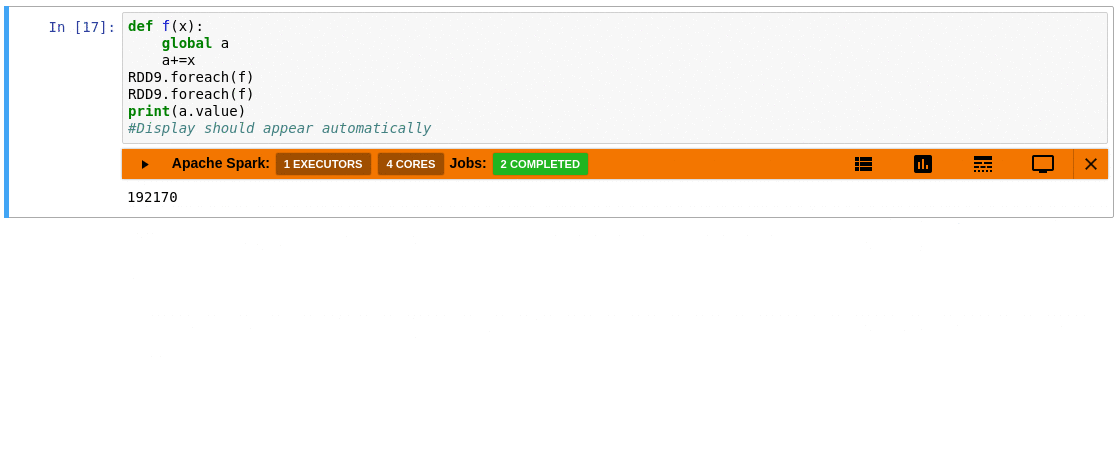
Sample of a Spark Monitor in operation:
Try out the sample notebook in the work directory to test out pyspark and plotly.
JupyterLab containers searchable and installable extensions. Click on the plugin icon in the left nav bar, and then click Enable after reading and understanding the warnings. This should not be required for Spark Monitor to function.
Passwords can be modified for both the Jovyan user in the Dockerfile or for the JupyerLab server in the docker-compose.yml.
To create a new JupyterLab password, in a JupyerLab terminal, start python3 and run the following:
>>> from notebook.auth.security import passwd
>>> passwd(algorithm='sha256')
Enter password:
Verify password:
'sha256:43139058e8c2:93c969c8d629577ee253084c018cf9b169d87e3191a61e846c61146f5e820a04'This can be be substituted in the docker-compose.yml file.
To create a different jovyan user password in the container, start a JupyterLab terminal and run the following:
echo 'passowrd' | openssl passwd -5 -stdinThe password can be substituted in the Dockerfile. The echo command needs the jovyan: user string and colon to precede the hashed password.