Key-Value storage system based on BitCask
Inspired by Paper
Download Project
$ git clone https://github.com/Zrealshadow/bitCask-kv.gitDownload dependencies
$ go mod download -jsonStart the Server
$go run main.goFor server configuration, we can change the file config.yaml under the config directory
Check api docs in Browser http://127.0.0.1:8080/swagger/index.html
the default port is 8080.
Create BitCaskBlock
$ curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/dbs?dbname=ttt'create a BitCaskBlock named ttt
Put Key-Value Pair into System
$ curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/db/ttt?key=Zeng&value=Lingze'Put Key "Zeng" and Value "Lingze" into System
Get Key-Value Pair from System
$ curl --location --request GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/db/ttt?key=Lingze'Delete Key-Value Pair from System
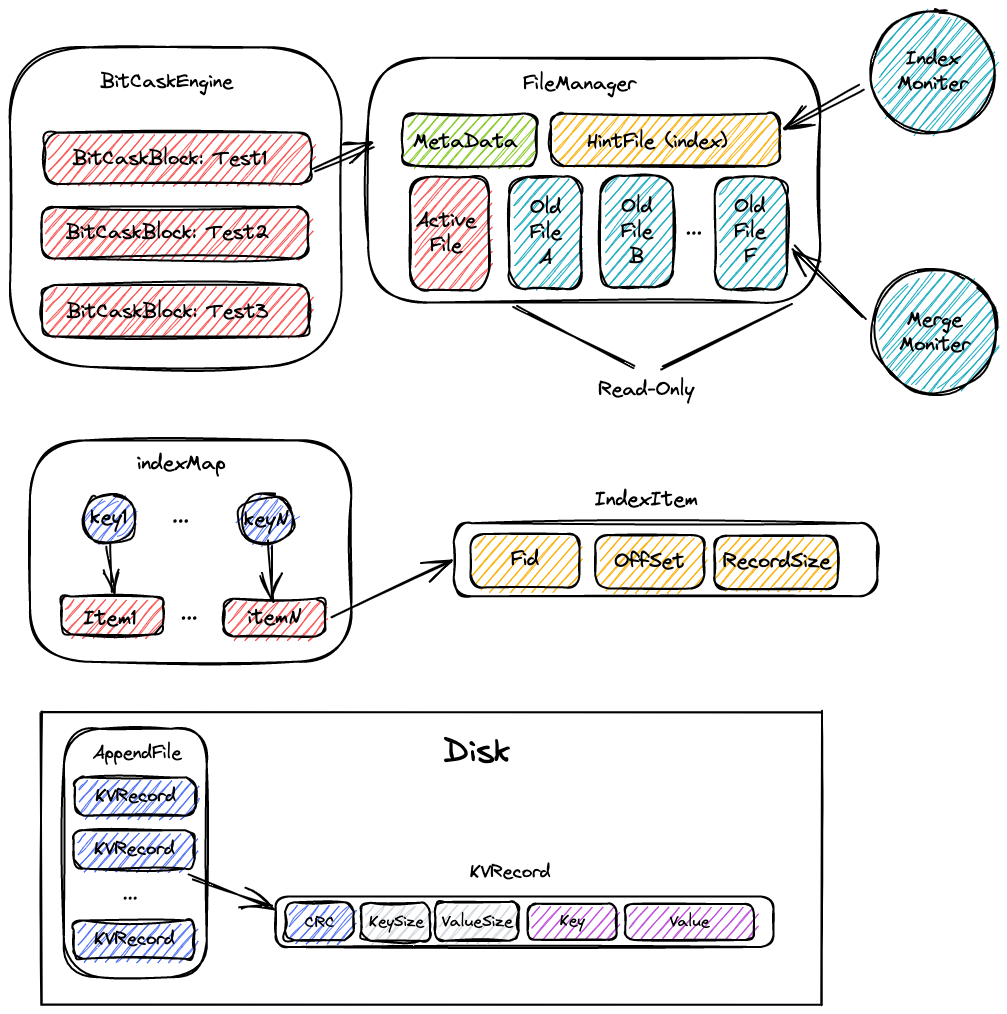
$ curl --location --request DELETE 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/db/ttt?key=Lingze'Firstly, the BitCaskEngine and BitCaskBlock is two class exposed to users. BitCaskEngine is like a whole DBSystem, BitCaskBlock is like a database in DBSystem. Data from different BitCaskBlock is isolated. User can index to BitCaskBlock by name and directly write data to it. Every BitCaskBlock hold a handler of FileManager, which is the most important part in the whole system.
metadata records some important information like the position of these appendfiles. The indexMap is stored in memory. Through indexing key in indexMap, we can find the corresponding record in which file and in which line and get the right value. However, if power off, this map will be lost, the system have to pass all appendfiles to rebuild these indexmap, in which the performance is not impressive . In order to improve this process, we can set a hintfile to record indexmap. Compared to all appendfiles, the size of the hintfile is much smaller. Re-building indexmap through hint file is much efficient. The index moniter is an goroutine which save updated indexmap into hint file periodically.
However, the operate of save meta data and index hint file is not atomic. The whole system can not keep consistent without other recovery mechanism. I will complete it in the future.
With the increase of data, many old files include the outdated records. We have to merge these older files to Alleviate the whole disk.
Instead of following the paper's method, my approach is to pass all records in old file, find records which are still useful and write them into active file. Compared to merge old files, my approach seems simpler in coding and can keep all files same size.
I also arrange a goroutine to periodically pass all files and check weather it need to be merged.
- Add Transaction concept and gurauntee ACID (The most important thing to do)
- Add Snapshot and WAL for index hint file save
- Add other apis mentioned in papers including
key-listresetclosesyncmerge