-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Remote control
Brutal Maze provides a INET (i.e. IPv4), STREAM (i.e. TCP) socket server which
can be enabled in the config file or by adding the --server CLI flag. After
binding to the given host and port, it will wait for a client to connect. Then,
in each cycle of the loop, the server will send current details of each object
(hero, walls, enemies and bullets), wait for the client to process the data and
return instruction for the hero to follow. Since there is no EOT (End of
Transfer) on a socket, messages sent and received between server and client
must must be strictly formatted as explained below.
First, the game will export its data to a byte sequence (which in this case, is simply a ASCII string without null-termination) of the length l. Before sending the data to the client, the server would send the number l padded to 7 digits.
Below is the meta structure of the data:
<Map height (nh)> <Number of enemies (ne)> <Number of bullets (nb)> <Score>
<nh lines describing visible part of the maze>
<One line describing the hero>
<ne lines describing ne enemies>
<nb lines describing nb bullets>
Visible parts of the maze with the width nw and the height nh are exported
as a byte map of nh lines and nw columns. Any character other than 0
represents a blocking cell, i.e. a wall.
To avoid floating point number in later description of other objects, each cell has the width (and height) of 100, which means the top left corner of the top left cell has the coordinates of (0, 0) and the bottom right vertex of the bottom right cell has the coordinates of (nw*100, nh*100).
6 properties of the hero are exported in one line, separated by 1 space, in the following order:
- Hero's color indicating the current HP of the hero, as shown in in the later section.
- X-coordinate, which will be in the range [0, nw * 100], cast to an integer.
- Y-coordinate, which will be in the range [0, nh * 100], cast to an integer. Note that the y-axis points up-side-down instead of pointing upward.
- Angle of the direction the hero is pointing to in degrees, cast to a nonnegative integer (from 0 to 360). Same note as above (the unit circle figure might help you understand this easier).
-
Flag showing if the hero can strike an attack,
0for no and1for yes. -
Flag showing if the hero can heal,
0for no and1for yes.

Each enemy exports these properties:
- Color indicating the type and current HP of the enemy, as shown in the table below.
- X-coordinate, which will be in the range [0, nw * 100], cast to an integer.
- Y-coordinate, which will be in the range [0, nh * 100], cast to an integer.
- Angle of the direction the hero is pointing to in degrees, cast to a nonnegative integer (from 0 to 360).
To shorten the data, each color (in the Tango palette) is encoded to a
lowercase letter or number 0. Different shades of a same color indicating
different HP of the characters.
| HP | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butter |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Orange |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Chocolate |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Chameleon |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Sky Blue |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Plum |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Scarlet Red |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Aluminium |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Bullets also export 4 properties like enemies:
-
Color indicating the type and potential damage of the bullet (from 0.0 to
1.0), encoded similarly to characters', except that Aluminium bullets only
have 4 colors
v,w,xand0. - X-coordinate, which will be in the range [0, nw * 100], cast to an integer.
- Y-coordinate, which will be in the range [0, nh * 100], cast to an integer.
- Angle of the bullet's flying direction in degrees, cast to a nonnegative integer (from 0 to 360).
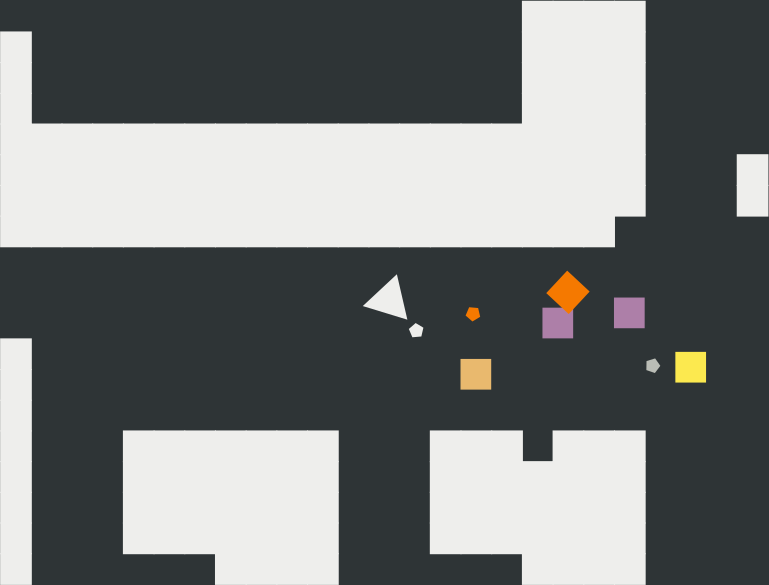
Above snapshot of the game is exported as:
19 5 3 180
00000000000000000vvvv0000
v0000000000000000vvvv0000
v0000000000000000vvvv0000
v0000000000000000vvvv0000
vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv0000
vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv000v
vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv000v
vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv00000
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
v000000000000000000000000
v000000000000000000000000
v000000000000000000000000
v000vvvvvvv000vvv0vvv0000
v000vvvvvvv000vvvvvvv0000
v000vvvvvvv000vvvvvvv0000
v000vvvvvvv000vvvvvvv0000
v000000vvvv000000vvvv0000
v 1267 975 47 0 1
p 1817 1050 45
g 1550 1217 45
a 2250 1194 45
p 2050 1017 45
e 1850 950 358
x 2126 1189 361
e 1541 1020 167
v 1356 1075 49
Every loop, the server receives no more than 7 bytes in this format:
<Movement> <Angle> <Attack>. Again, these values need to be specially
encoded.
This is the most awkward one. As we can all imagine, there are 9 different
directions for the hero to move. If we represent them as two-dimensional
vector, at least 3 characters will be needed to describe such a simple thing,
e.g. 1 0 for m = (1, 0), and in the worst-case scenario m = (-1, -1), we will
need to use 5: -1 -1. 40 bits used to carry a 4-bit piece of data, freaking
insane, right? So instead, we decided to slightly encode it like this:
| Direction | Left | Nil | Right |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Nil | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Down | 6 | 7 | 8 |
Direction to point to hero to, might be useful to aim or to perform close-range attack manually. This value should also be converted to degrees and cast to a nonnegative integer.
Attack can be either of the three values:
- Do nothing
- Long-range attack
- Close-range attack
Simple, huh? Though be aware that this won't have any effect if the hero cannot strike an attack yet (as described in above section about Server output).
- Create INET, STREAMing socket s
- Connect s to the address
host:portwhich the server is bound to - Receive length l of data
- If l > 0, close s and quit
- Receive the data
- Process the data
- Send instruction for the hero to the server and go back to step 3
Your AI should try to not only reach the highest score possible, but also in the smallest amount of time. For convenience purpose, the server will log these values to stdout.
There are samples of client implementations in different languages in client-examples directory (more are coming).