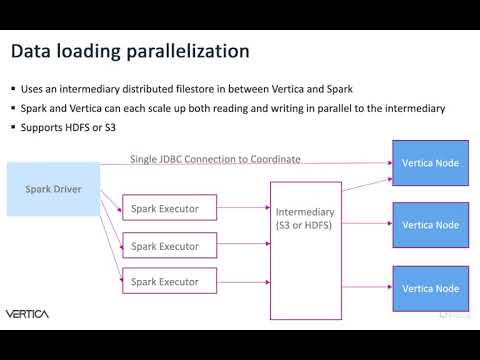
This component acts as a bridge between Spark and Vertica, allowing the user to either retrieve data from Vertica for processing in Spark, or store processed data from Spark into Vertica.
Why is this connector desired instead of using a more generic JDBC connector? A few reasons:
- Vertica-specific syntax and features. This connector can support things like Vertica projections
- Authentication to the Vertica server
- Segmentation. We can use the way that Vertica segments data to inform our operations
- Ability to use other technology as an intermediary for data transfer. This is necessary for maximizing performance of parallel loads
This connector is built as a JAR file to be sourced in your spark application. This is accessible through Maven Central or you can build the JAR yourself with sbt assembly.
The connector relies on a distributed filesystem, such as HDFS, to act as a bridge between Spark and Vertica. This is done to allow for maximum performance at high scale.
The connector creates a JDBC connection to Vertica in order to manage the process of importing or exporting data (the data does not pass over this connection).
To get started with using the connector, we'll need to make sure all the prerequisites are in place. These are:
- Vertica (10.1.1-0 or higher)
- Spark (3.0.0 or higher)
- An HDFS cluster or HDFS-compatible filesystem (S3, Google Cloud Storage, etc), for use as an intermediary between Spark and Vertica
- A Spark application, either running locally for quick testing, or running on a Spark cluster. If using S3, Spark must be using hadoop 3.3
For an easier quick test of the connector using a Docker environment, see this guide for running our examples.
Follow the Vertica Documentation for steps on installing Vertica.
The connector has been tested against Vertica 10.1.1-0 and higher.
The connector requires Spark 3.0.0 or higher.
There are several examples of Spark programs that use this connector in the examples directory.
The methods for creating a Spark cluster are documented here.
Once you have a Spark cluster, you can run such an application with spark-submit, including the connector JAR.
spark-submit --master spark://cluster-url.com:7077 --deploy-mode cluster sparkconnectorprototype-assembly-0.1.jarAn HDFS setup can have various configurations, for details of what might best fit your infrastructure the HDFS Architecture Guide is recommended.
For a quick start, you can either check out our guide on setting up a single-node HDFS or if you are just wanting a quick test run, you can use an HDFS container in Docker as documented in our contributing guide.
However you set up HDFS, Vertica needs to have a copy of the Hadoop configuration (location of hdfs-site.xml and core-site.xml). Each Vertica node must also have access. Options for this are to either copy said configuration to /etc/hadoop/conf on those machines, or to tell Vertica where to find the configuration like so:
ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET HadoopConfDir = '/hadoop/conf/location/';The connector requires Java 8 (8u92 or later) or Java 11.
For the Spark Connector, Spark 3.0.0 and above use Scala 2.12. You will need to use a compatible Scala version (2.12.x).
The connector requires HDFS, or any file systems that implements Hadoop File Systems API, for use when accessing Vertica tables.
Using the connector in Spark is straightforward. It requires the data source name, an options map, and, if writing to Vertica, a Spark Save Mode.
Example read and write using the connector:
val opts = Map(
"host" -> "vertica_hostname",
"user" -> "vertica_user",
"db" -> "db_name",
"password" -> "db_password",
"staging_fs_url" -> "hdfs://hdfs-url:7077/data",
"table" -> "tablename"
)
// Create data and put it in a dataframe
val schema = new StructType(Array(StructField("col1", IntegerType)))
val data = Seq(Row(77))
val df = spark.createDataFrame(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(data), schema).coalesce(1)
val mode = SaveMode.ErrorIfExists
// Write the dataframe to Vertica
df.write.format("com.vertica.spark.datasource.VerticaSource").options(opts ).mode(mode).save()
// Read it back from Vertica
val dfRead: DataFrame = spark.read.format("com.vertica.spark.datasource.VerticaSource").options(opts).load()The Spark connector converts all Spark SQL Strings to Vertica VARCHAR values. The length of these VARCHAR values defaults to 1024 (octet length). You can change the octet length of the VARCHAR that is stored in Vertica by setting the strlen option in the option Map.
The connector, using an intermediary file location between Spark and Vertica, may require both sides to have write access to the intermediary location used.
The default permission (configurable via the file_permissions option) is 700, or access only for the given user. This is the default for security reasons, but will cause issues if your user running Spark and database user are different.
There are a few ways to solve this:
- Change the
file_permissionsoption to a suitable value. Warning: setting this to777means any user with filesystem access could read the data being transferred. Setting this to770could work if users on each side of the operation share a group - Change the operation to use the same user for Spark and the database
- Use
export HADOOP_USER_NAME=<vertica_db_name>to have Spark's Hadoop communication use the same user as the database
Below is a detailed list of connector options that are used in the options map:
| Configuration Option | Possible Values | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
table |
String | The name of the target Vertica table to save your Spark DataFrame. New: Should parse schema from tablename if specified with schema.table. | No (Either or with Query) | |
query |
String | An SQL statement to be used in place of the connector's generated query when reading data from Vertica. This is useful if in cases where a more complex query is needed to export the data from Vertica. For example, it can be used to specify the exported data to be a join between two tables. The query cannot return complex type results. | No (Either or with Table) | |
db |
String | The name of the Vertica Database. | Yes | |
backup_server_node |
String | A comma-separated list of vertica backup nodes. The host name or IP can optionally be followed by a colon and a port number. If not supplied, defaults to the standard Vertica port number (5433). |
No | Empty |
user |
String | The name of the Vertica user. This user must have CREATE and INSERT privileges in the Vertica schema. The schema defaults to public, but may be changed using the dbschema optional parameter. |
Yes | |
password |
String | The password for the Vertica user. | Yes (No, if using SSO) | |
host |
String | The hostname of a Vertica node. This value is used to make the initial connection to Vertica and look up all the other Vertica node IP addresses. You can provide a specific IP address or a resolvable name such as myhostname.com. |
Yes | |
dbschema |
String | The schema space for the Vertica table. | No | public |
port |
Int | The Vertica port. | No | 5433 |
failed_rows_percent_tolerance |
Number | The tolerance level for failed rows, as a percentage. For example, to specify that the job fails if greater than 10% of the rows are rejected, specify this value as 0.10 for 10% tolerance. |
No | 0.00 |
strlen |
Int | The string length. Use this option to increase (or decrease) the default length when saving Spark StringType to Vertica VARCHAR type. Used to determine whether to use VARCHAR or LONG VARCHAR. This option could also be used to override the default size (1024) of VARCHAR columns when creating an external table from existing data. |
No | 1024 |
array_length |
Int | The default number of array elements. When specified, sets the default number of elements when saving Spark ArrayType to Vertica Array type. This is applied to all nested arrays. By default, this option is set to 0 and will use Vertica's default array length. Refer to the Vertica documentation for more details. |
No | 0 |
target_table_sql (previously target_table_ddl) |
String | An SQL statement to be used in place of the connector's when a table is to be created when writing to Vertica. Useful when you wants the data to be written into a table with a different schema than that of the source dataframe. Note that the table name should matches with that of the table option. |
No | |
copy_column_list |
String | A comma-separated list of columns for use in the COPY statement when writing data to Vertica. Useful in situations where the Vertica table and Spark dataframe do not have to have a valid schema for a COPY statement (e.g. different column names). See documentation. | No | |
num_partitions (previously numpartitions) |
Int | The number of Spark partitions used when reading from Vertica. Each of these will correspond to a task with its own JDBC connection. Performance testing has indicated that the ideal number of partitions is 4*N where N is the number nodes in the Vertica cluster for the direct read method. Most efficient partition count for intermediate method may vary, will require testing and may be a tradeoff of memory vs time. | No | 1 per exported parquet file |
staging_fs_url (previously hdfs_url) |
URL (String) | The fully-qualified path to a directory in HDFS or S3 that will be used as a data staging area. For example, hdfs://myhost:8020/data/test. For S3, the URL should begin with s3a://. The connector first saves the DataFrame in its entirety to this location before loading into Vertica. The data is saved in Parquet format, and the files are saved in a directory specific to each job. This directory is then deleted when the job completes. Note that you need additional configuration changes to use HDFS. You must first configure all nodes to use HDFS. See Configuring the hdfs Scheme. Note: this option is also used to specify the filepath for external tables, where the external table may be loaded or saved to this location. Please see the create_external_table option for more details. |
Yes | |
merge_key |
String | In order to execute a merge statement in our Spark Connector, the user needs to pass in a merge key, which will be a list of comma-separated column attributes to join the existing table and temporary table on (e.g. foo, bar, baz or foo,bar,baz). Note: the merge key must be unique in the dataframe for the merge to work. Additionally, the number of columns in the dataframe must be less than or equal to the number of columns in the target table. If the number of columns in the dataframe are less than the target table and the names of the columns differ, use copy_column_list to match the dataframe columns against the target table columns. Last note: while you may use copy_column_list to get around differing column names between the dataframe and existing table, the column names of the merge_key must match in both schemas. |
No | |
create_external_table |
new-data / true / existing-data (String) |
An option to create an external table, either out of existing parquet data in HDFS or by writing data from Spark to HDFS. For the latter use-case, specify this option as new-data or true. For the former use-case, specify this option as existing-data. For both cases, you must specify either the location of the external table or location of existing data in the staging_fs_url connector option (e.g. webhdfs://hdfs:50070/data/data.parquet/). For existing-data, ensure that the Spark dataframe you are writing is empty. Note: When creating an external table from existing data, partitioned columns will require you provide a partial schema detailing those columns. Please see the examples README for further details. |
No | |
truncate |
Boolean | When set to true the connector will truncate a table rather than drop it in overwrite mode. |
No | false |
save_job_status_table |
Boolean | When set, the job status table will be created and maintained in Vertica per user. Both writes and external tables are recorded in this table. | No | false |
prevent_cleanup |
Boolean | An option to prevent cleanup in the intermediary filestore layer during a read or a write. The default value is false, but this may be set to true to keep parquet files after a Spark job is ran. |
No | false |
time_operations |
Boolean | Timing information will be logged as per the Troubleshooting Guide. | No | true |
json |
Boolean | If true, the connector will always export data as JSON when reading. |
No | false |
kerberos_service_name |
String | The Kerberos service name, as specified when creating the service principal. | No (Yes, if using Kerberos) | |
kerberos_host_name |
String | The Kerberos host name, as specified when creating the service principal. | No (Yes, if using Kerberos) | |
jaas_config_name |
String | The name of the JAAS configuration used for Kerberos authentication. | No | verticajdbc |
tls_mode |
disable / require / verify-ca / verify-full (String) |
When not set to disable, connections with Vertica are encrypted. See the Vertica documentation for more details on what each mode does. |
No | disable |
key_store_path |
Filepath (String) | The local path to a .JKS file containing your private keys and their corresponding certificate chains. | No | |
key_store_password |
String | The password protecting the keystore file. If individual keys are also encrypted, the keystore file password must match the password for a key within the keystore. | No | |
trust_store_path |
String | The local path to a .JKS truststore file containing certificates from authorities you trust. | No | |
trust_store_password |
String | The password protecting the truststore file. | No | |
file_permissions |
String | Unix file permissions used for the intermediary filestore, can be in octal format (e.g. 750) or user-group-other (e.g. -rwxr--r--). |
No | 770 |
max_file_size_export_mb |
Int | Vertica maximum export file size in MB. | No | 4096 |
max_row_group_size_export_mb |
Int | Vertica maximum row group file size in MB. | No | 16 |
aws_access_key_id |
String | The access key ID for S3. Specifying this option sets the access key ID at the session level. Alternatively, you can set the spark.hadoop.fs.s3a.access.key option in the Spark configuration or the environment variable AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID. |
No (Yes if aws_secret_access_key is specified) |
|
aws_secret_access_key |
String | The secret access key for S3. Specifying this option sets the secret access key at the session level. Alternatively, you can set the spark.hadoop.fs.s3a.access.key option in the Spark configuration or the environment variable AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY. |
No (Yes if aws_access_key_id is specified) |
|
aws_region |
String | The AWS region for S3. Specifying this option sets the secret access key at the session level. Alternatively, you can set the environment variable AWS_DEFAULT_REGION. |
No | |
aws_session_token |
String | An AWS session token. Specifying this option sets the session token at the session level. Alternatively, you can set the spark.hadoop.fs.s3a.session.token option in the Spark configuration or the environment variable AWS_SESSION_TOKEN. |
No | |
aws_credentials_provider |
String | The AWS credentials provider. For example, if you want to use the IAMInstanceCredentialsProvider, you would specify this option as org.apache.hadoop.fs.s3a.auth.IAMInstanceCredentialsProvider. Specifying this option sets the AWS credentials provider option in the Hadoop configuration. Alternatively, you can set the spark.hadoop.fs.s3a.aws.credentials.provider option in the Spark configuration. If left blank, Hadoop will default to trying SimpleAWSCredentialsProvider, EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider, and InstanceProfileCredentialsProvider in order. Please note that we have only tested the connector with SimpleAWSCredentialsProvider and IAMInstanceCredentialsProvider, so other credential providers will have limited support. |
No | |
aws_endpoint |
String | The AWS endpoint to use, if not the default amazon AWS instance. Can be used if interacting with a different data store that implements the S3 API. | No | |
aws_enable_ssl |
Boolean | If true then SSL is used for AWS connections. Defaults to true. Only change this if using an endpoint that does not use https. In older versions of Vertica (before 11.0.x) this must be set at the database level. Use ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET AWSEnableHttps=0 for this. For Vertica 11.0.x and later, simply set this connector option which will configure the option at the session level. |
No | true |
aws_enable_path_style |
Boolean | Whether path style access should be used (e.g. https://s3.region.amazonaws.com/bucket). Defaults to false, meaning that virtual-host style access is used instead (e.g. https://bucket.s3.region.amazonaws.com). Only change this if using an endpoint that does not support or is not configured to use virtual-host style access. |
No | false |
gcs_hmac_key_id |
String | The GCS S3 interoperability key id for using GCS as intermediary storage. It is used by Vertica to access GCS. If specified, gcs_hmac_key_id is also required. Can also be specified as a Spark configuration option or in the environment variable GCS_HMAC_KEY_ID. |
No (Yes, if gcs_hmac_key_secret was specified) |
|
gcs_hmac_key_secret |
String | The GCS S3 interoperability key secret for using GCS as intermediary storage. It is used by Vertica to access GCS. If specified, gcs_hmac_key_secret is also required. Can also be specified as a Spark configuration option or in the environment variable GCS_HMAC_KEY_SECRET. |
No (Yes, if gcs_hmac_key_id was specified) |
|
gcs_service_keyfile |
String | The path to a GCS service account JSON keyfile. Used for configuring GCS as intermediary storage. Alternatively, you can specify the key path in GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS environment variable or in the Spark configuration option fs.gs.auth.service.account.json.keyfile. |
No | |
gcs_service_key_id |
String | The GCS service account key id. For use instead of specifying a keyfile path. The value be found within the service account JSON keyfile field private_key_id. Alternatively, you can use the Spark configuration fs.gs.auth.service.account.private.key.id or the environment variable GCS_SERVICE_KEY_ID. |
No (Yes, if gcs_service_key and gcs_service_email were specified) |
|
gcs_service_key |
String | The GCS service account key. For use instead of specifying a keyfile path. The value be found within the service account JSON keyfile field private_key. Alternatively, you can use the Spark configuration fs.gs.auth.service.account.private.key or the environment variable GCS_SERVICE_KEY. |
No (Yes, if gcs_service_key_id and gcs_service_email were specified) |
|
gcs_service_email |
String | The GCS service account email. For use instead of specifying a keyfile path. The value be found within the service account JSON keyfile field client_email, you can use the Spark configuration fs.gs.auth.service.account.email or the environment variable GCS_SERVICE_EMAIL. |
No (Yes, if gcs_service_key and gcs_service_key_id were specified) |
Note: If you are using the S3 properties, the connector options have priority over the Spark configuration, which has priority over the environment variables.
Since the connector implements Spark's DataSource V2 interfaces, it also supports pushdowns, specifically filter, columns, and aggregates. All pushdowns are handled automatically by Spark and does not require any configurations. Note that aggregate pushdown is only supported for Spark 3.2.0, and not all aggregates are supported.
The connector supports reading/writing:
- Row type columns
- Complex arrays (any arrays that are not 1D arrays of primitives) columns
When reading complex types, all of the data will be exported as JSON files instead of Parquet files.
For map type, the connector can only write to an external table but cannot read them. Vertica suggests using Array[Row(key, value)] instead for use in internal tables.
Writing complex data types requires at least Vertica 11.x and Vertica JDBC Driver 11.
Reading complex data types requires at least Vertica 11.1.1-0.
Refer to the examples for usage demonstration.
Note: If the connector option query is used, the specified query cannot return complex types.
| Spark Dataframe | Vertica Tables |
|---|---|
| Array | Array |
| Array | Set |
| Struct | Row |
| Map | Map (only for external tables) |
Be aware that Vertica has a number of restrictions on the use of these complex types (this list is not exhaustive):
- Arrays and Sets do not support Long types
- When reading complex types, binary types cannot be present in the data. This is due to Vertica's JSON export limitation
JDBC does not define a data type similar to Vertica SET.
Thus, the exported data will be of array type, with Spark's column metadata containing is_vertica_set = true if it is a set.
- When writing to Vertica using overwrite mode, the recreated table will have the column as a set type. Unique elements are only checked once Vertica start loading data from staging area
- When writing without overwrite mode, the connector will not recreate the table and the column type is unchanged
- When reading Vertica tables, the array column's metadata will contains the above value if it is a set in Vertica
For Vertica 10, only writing native arrays (1D arrays of primitive) is supported.
If you would like to try out the connector, we have several example applications you can run in the examples folder.
For information on how to configure Kerberos and TLS with the connector, see the Kerberos user guide and TLS user guide files in the root of this repository.
For information on tuning performance, see the performance-tests section.
For information on troubleshooting, see the troubleshooting guide.
If using S3 rather than HDFS, the Spark cluster must be running with hadoop 3.3. Our S3 user guide goes over how to configure this.
Vertica Spark Connector Overview