参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
字典 wordList 中从单词 beginWord 和 endWord 的 转换序列 是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
- 序列中第一个单词是 beginWord 。
- 序列中最后一个单词是 endWord 。
- 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
- 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典 wordList 中的单词。
- 给你两个单词 beginWord 和 endWord 和一个字典 wordList ,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的 最短转换序列 中的 单词数目 。如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
示例 1:
- 输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
- 输出:5
- 解释:一个最短转换序列是 "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog", 返回它的长度 5。
示例 2:
- 输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
- 输出:0
- 解释:endWord "cog" 不在字典中,所以无法进行转换。
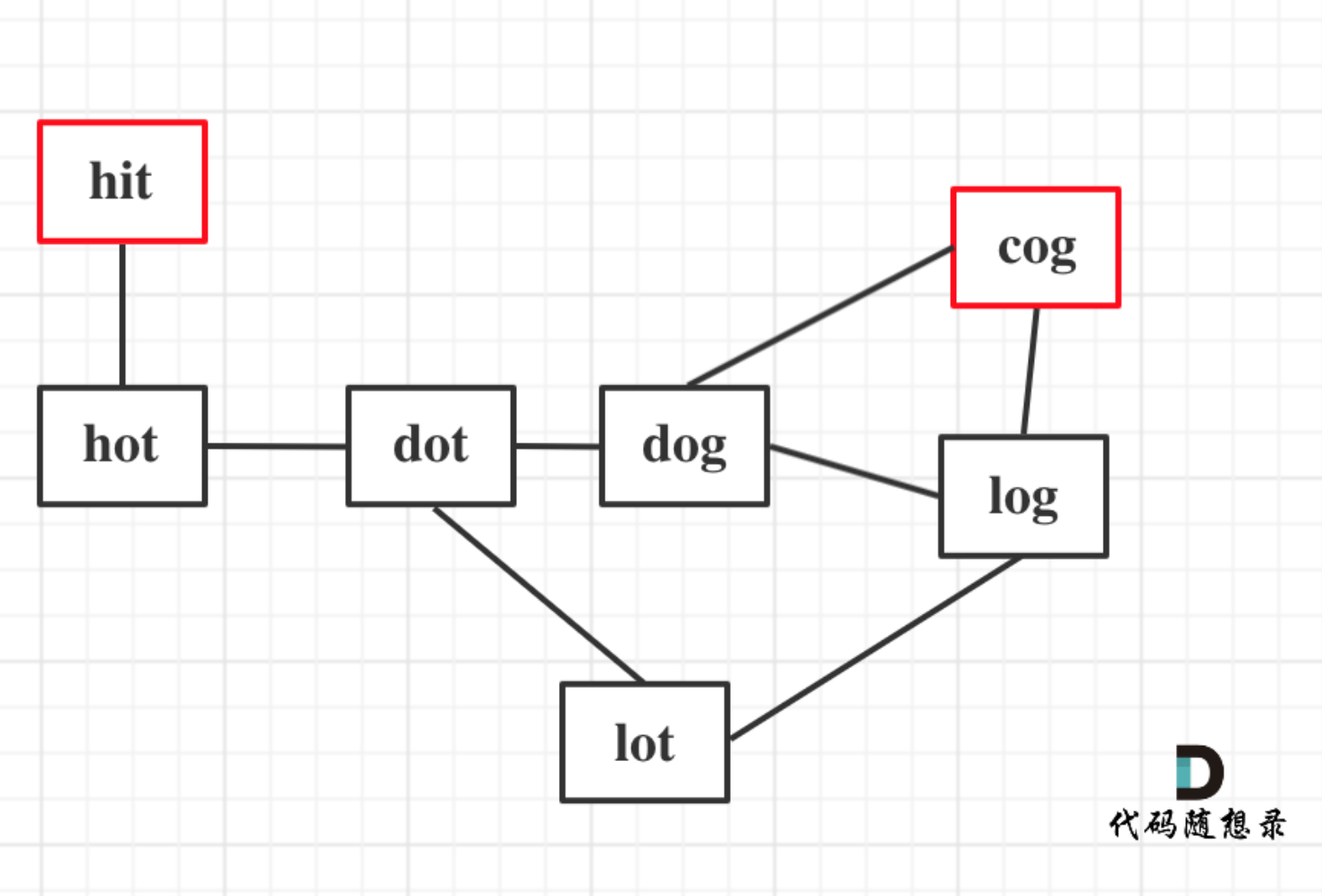
以示例1为例,从这个图中可以看出 hit 到 cog的路线,不止一条,有三条,一条是最短的长度为5,两条长度为6。
本题只需要求出最短路径的长度就可以了,不用找出路径。
所以这道题要解决两个问题:
- 图中的线是如何连在一起的
- 起点和终点的最短路径长度
首先题目中并没有给出点与点之间的连线,而是要我们自己去连,条件是字符只能差一个,所以判断点与点之间的关系,要自己判断是不是差一个字符,如果差一个字符,那就是有链接。
然后就是求起点和终点的最短路径长度,这里无向图求最短路,广搜最为合适,广搜只要搜到了终点,那么一定是最短的路径。因为广搜就是以起点中心向四周扩散的搜索。
本题如果用深搜,会比较麻烦,要在到达终点的不同路径中选则一条最短路。 而广搜只要达到终点,一定是最短路。
另外需要有一个注意点:
- 本题是一个无向图,需要用标记位,标记着节点是否走过,否则就会死循环!
- 本题给出集合是数组型的,可以转成set结构,查找更快一些
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
// 将vector转成unordered_set,提高查询速度
unordered_set<string> wordSet(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());
// 如果endWord没有在wordSet出现,直接返回0
if (wordSet.find(endWord) == wordSet.end()) return 0;
// 记录word是否访问过
unordered_map<string, int> visitMap; // <word, 查询到这个word路径长度>
// 初始化队列
queue<string> que;
que.push(beginWord);
// 初始化visitMap
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(beginWord, 1));
while(!que.empty()) {
string word = que.front();
que.pop();
int path = visitMap[word]; // 这个word的路径长度
for (int i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
string newWord = word; // 用一个新单词替换word,因为每次置换一个字母
for (int j = 0 ; j < 26; j++) {
newWord[i] = j + 'a';
if (newWord == endWord) return path + 1; // 找到了end,返回path+1
// wordSet出现了newWord,并且newWord没有被访问过
if (wordSet.find(newWord) != wordSet.end()
&& visitMap.find(newWord) == visitMap.end()) {
// 添加访问信息
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(newWord, path + 1));
que.push(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};当然本题也可以用双向BFS,就是从头尾两端进行搜索,大家感兴趣,可以自己去实现,这里就不再做详细讲解了。
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
HashSet<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList); //转换为hashset 加快速度
if (wordSet.size() == 0 || !wordSet.contains(endWord)) { //特殊情况判断
return 0;
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //bfs 队列
queue.offer(beginWord);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); //记录单词对应路径长度
map.put(beginWord, 1);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String word = queue.poll(); //取出队头单词
int path = map.get(word); //获取到该单词的路径长度
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { //遍历单词的每个字符
char[] chars = word.toCharArray(); //将单词转换为char array,方便替换
for (char k = 'a'; k <= 'z'; k++) { //从'a' 到 'z' 遍历替换
chars[i] = k; //替换第i个字符
String newWord = String.valueOf(chars); //得到新的字符串
if (newWord.equals(endWord)) { //如果新的字符串值与endWord一致,返回当前长度+1
return path + 1;
}
if (wordSet.contains(newWord) && !map.containsKey(newWord)) { //如果新单词在set中,但是没有访问过
map.put(newWord, path + 1); //记录单词对应的路径长度
queue.offer(newWord);//加入队尾
}
}
}
}
return 0; //未找到
}// Java 双向BFS
class Solution {
// 判断单词之间是否之差了一个字母
public boolean isValid(String currentWord, String chooseWord) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < currentWord.length(); i++)
if (currentWord.charAt(i) != chooseWord.charAt(i)) ++count;
return count == 1;
}
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
if (!wordList.contains(endWord)) return 0; // 如果 endWord 不在 wordList 中,那么无法成功转换,返回 0
// ansLeft 记录从 beginWord 开始 BFS 时能组成的单词数目
// ansRight 记录从 endWord 开始 BFS 时能组成的单词数目
int ansLeft = 0, ansRight = 0;
// queueLeft 表示从 beginWord 开始 BFS 时使用的队列
// queueRight 表示从 endWord 开始 BFS 时使用的队列
Queue<String> queueLeft = new ArrayDeque<>(), queueRight = new ArrayDeque<>();
queueLeft.add(beginWord);
queueRight.add(endWord);
// 从 beginWord 开始 BFS 时把遍历到的节点存入 hashSetLeft 中
// 从 endWord 开始 BFS 时把遍历到的节点存入 hashSetRight 中
Set<String> hashSetLeft = new HashSet<>(), hashSetRight = new HashSet<>();
hashSetLeft.add(beginWord);
hashSetRight.add(endWord);
// 只要有一个队列为空,说明 beginWord 无法转换到 endWord
while (!queueLeft.isEmpty() && !queueRight.isEmpty()) {
++ansLeft;
int size = queueLeft.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String currentWord = queueLeft.poll();
// 只要 hashSetRight 中存在 currentWord,说明从 currentWord 可以转换到 endWord
if (hashSetRight.contains(currentWord)) return ansRight + ansLeft;
for (String chooseWord : wordList) {
if (hashSetLeft.contains(chooseWord) || !isValid(currentWord, chooseWord)) continue;
hashSetLeft.add(chooseWord);
queueLeft.add(chooseWord);
}
}
++ansRight;
size = queueRight.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String currentWord = queueRight.poll();
// 只要 hashSetLeft 中存在 currentWord,说明从 currentWord 可以转换到 beginWord
if (hashSetLeft.contains(currentWord)) return ansLeft + ansRight;
for (String chooseWord : wordList) {
if (hashSetRight.contains(chooseWord) || !isValid(currentWord, chooseWord)) continue;
hashSetRight.add(chooseWord);
queueRight.add(chooseWord);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
wordSet = set(wordList)
if len(wordSet)== 0 or endWord not in wordSet:
return 0
mapping = {beginWord:1}
queue = deque([beginWord])
while queue:
word = queue.popleft()
path = mapping[word]
for i in range(len(word)):
word_list = list(word)
for j in range(26):
word_list[i] = chr(ord('a')+j)
newWord = "".join(word_list)
if newWord == endWord:
return path+1
if newWord in wordSet and newWord not in mapping:
mapping[newWord] = path+1
queue.append(newWord)
return 0
func ladderLength(beginWord string, endWord string, wordList []string) int {
wordMap, que, depth := getWordMap(wordList, beginWord), []string{beginWord}, 0
for len(que) > 0 {
depth++
qLen := len(que) // 单词的长度
for i := 0; i < qLen; i++ {
word := que[0]
que = que[1:] // 首位单词出队
candidates := getCandidates(word)
for _, candidate := range candidates {
if _, exist := wordMap[candidate]; exist { // 用生成的结果集去查询
if candidate == endWord {
return depth + 1
}
delete(wordMap, candidate) // 删除集合中的用过的结果
que = append(que, candidate)
}
}
}
}
return 0
}
// 获取单词Map为后续的查询增加速度
func getWordMap(wordList []string, beginWord string) map[string]int {
wordMap := make(map[string]int)
for i, word := range wordList {
if _, exist := wordMap[word]; !exist {
if word != beginWord {
wordMap[word] = i
}
}
}
return wordMap
}
// 用26个英文字母分别替换掉各个位置的字母,生成一个结果集
func getCandidates(word string) []string {
var res []string
for i := 0; i < 26; i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(word); j++ {
if word[j] != byte(int('a')+i) {
res = append(res, word[:j]+string(int('a')+i)+word[j+1:])
}
}
}
return res
}var ladderLength = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
// 将wordList转成Set,提高查询速度
const wordSet = new Set(wordList);
// Set元素个数为0 或者 endWord没有在wordSet出现,直接返回0
if (wordSet.size === 0 || !wordSet.has(endWord)) return 0;
// 记录word是否访问过
const visitMap = new Map();// <word, 查询到这个word路径长度>
// 初始化队列
const queue = [];
queue.push(beginWord);
// 初始化visitMap
visitMap.set(beginWord, 1);
while(queue.length !== 0){
let word = queue.shift(); // 删除队首元素,将它的值存放在word
let path = visitMap.get(word); // 这个word的路径长度
for(let i = 0; i < word.length; i++){ // 遍历单词的每个字符
for (let c = 97; c <= 122; c++) { // 对应26个字母ASCII值 从'a' 到 'z' 遍历替换
// 拼串得到新的字符串
let newWord = word.slice(0, i) + String.fromCharCode(c) + word.slice(i + 1);
if(newWord === endWord) return path + 1; // 找到了end,返回path+1
// wordSet出现了newWord,并且newWord没有被访问过
if(wordSet.has(newWord) && !visitMap.has(newWord)) {
// 添加访问信息
visitMap.set(newWord, path + 1);
queue.push(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
};function ladderLength(
beginWord: string,
endWord: string,
wordList: string[]
): number {
const words = new Set(wordList);
if (!words.has(endWord)) return 0;
if (beginWord.length === 1) return 2;
let current = new Set([beginWord]);
let rightcurrent = new Set([endWord]);
words.delete(endWord);
let step = 1;
while (current.size) {
if (current.size > rightcurrent.size) {
[current, rightcurrent] = [rightcurrent, current];
}
const temp: Set<string> = new Set();
for (const word of current) {
for (const right of rightcurrent) {
if (diffonechar(word, right)) {
return step + 1;
}
}
for (const other of words) {
if (diffonechar(other, word)) {
temp.add(other);
words.delete(other);
}
}
}
if (temp.size === 0) return 0;
current = temp;
step = step + 1;
}
return 0;
}
function diffonechar(word1: string, word2: string): boolean {
let changes = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < word1.length; i++) {
if (word1[i] != word2[i]) changes += 1;
}
return changes === 1;
}