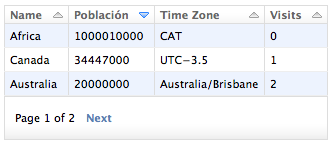
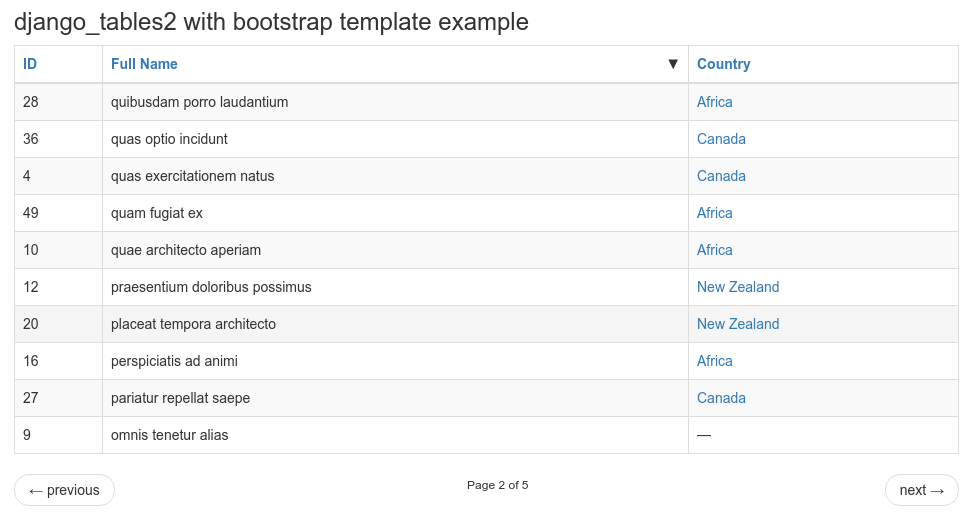
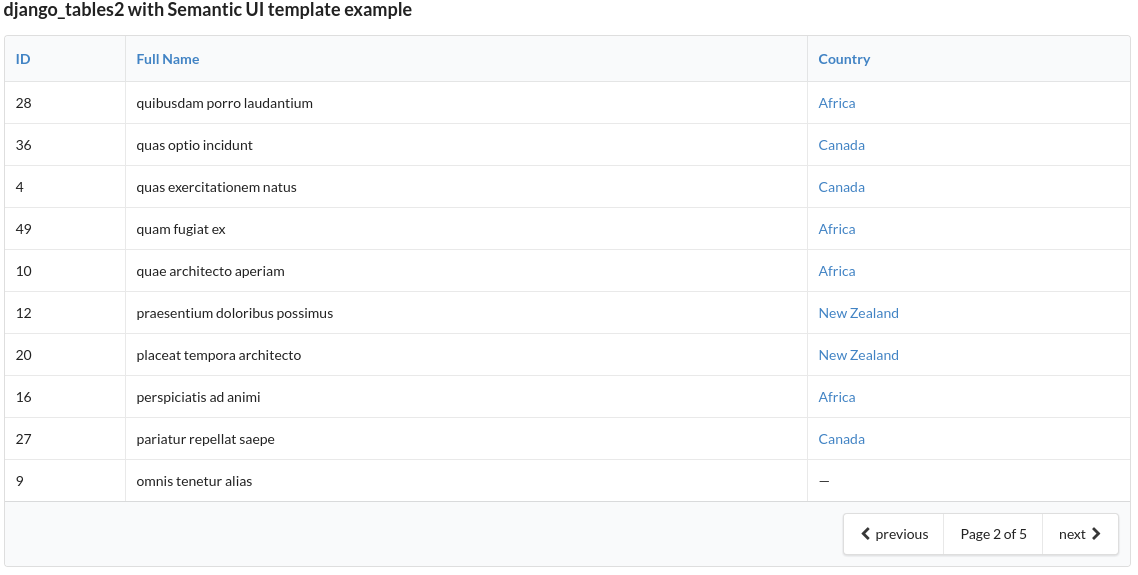
django-tables2 simplifies the task of turning sets of data into HTML tables. It has native support for pagination and sorting. It does for HTML tables what django.forms does for HTML forms. e.g.
Its features include:
- Any iterable can be a data-source, but special support for Django querysets is included.
- The builtin UI does not rely on JavaScript.
- Support for automatic table generation based on a Django model.
- Supports custom column functionality via subclassing.
- Pagination.
- Column based table sorting.
- Template tag to enable trivial rendering to HTML.
- Generic view mixin.
About the app:
- Available on pypi
- Tested with python 2.7, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5 and Django 1.8, 1.9, Travis CI
- Documentation on readthedocs.org
- Bug tracker
Start by adding django_tables2 to your INSTALLED_APPS setting like this:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
...,
'django_tables2',
)Creating a table for a model Simple is as simple as:
import django_tables2 as tables
class SimpleTable(tables.Table):
class Meta:
model = SimpleThis would then be used in a view:
def simple_list(request):
queryset = Simple.objects.all()
table = SimpleTable(queryset)
return render(request, 'simple_list.html', {'table': table})And finally in the template:
{% load django_tables2 %}
{% render_table table %}
This example shows one of the simplest cases, but django-tables2 can do a lot more! Check out the documentation for more details.