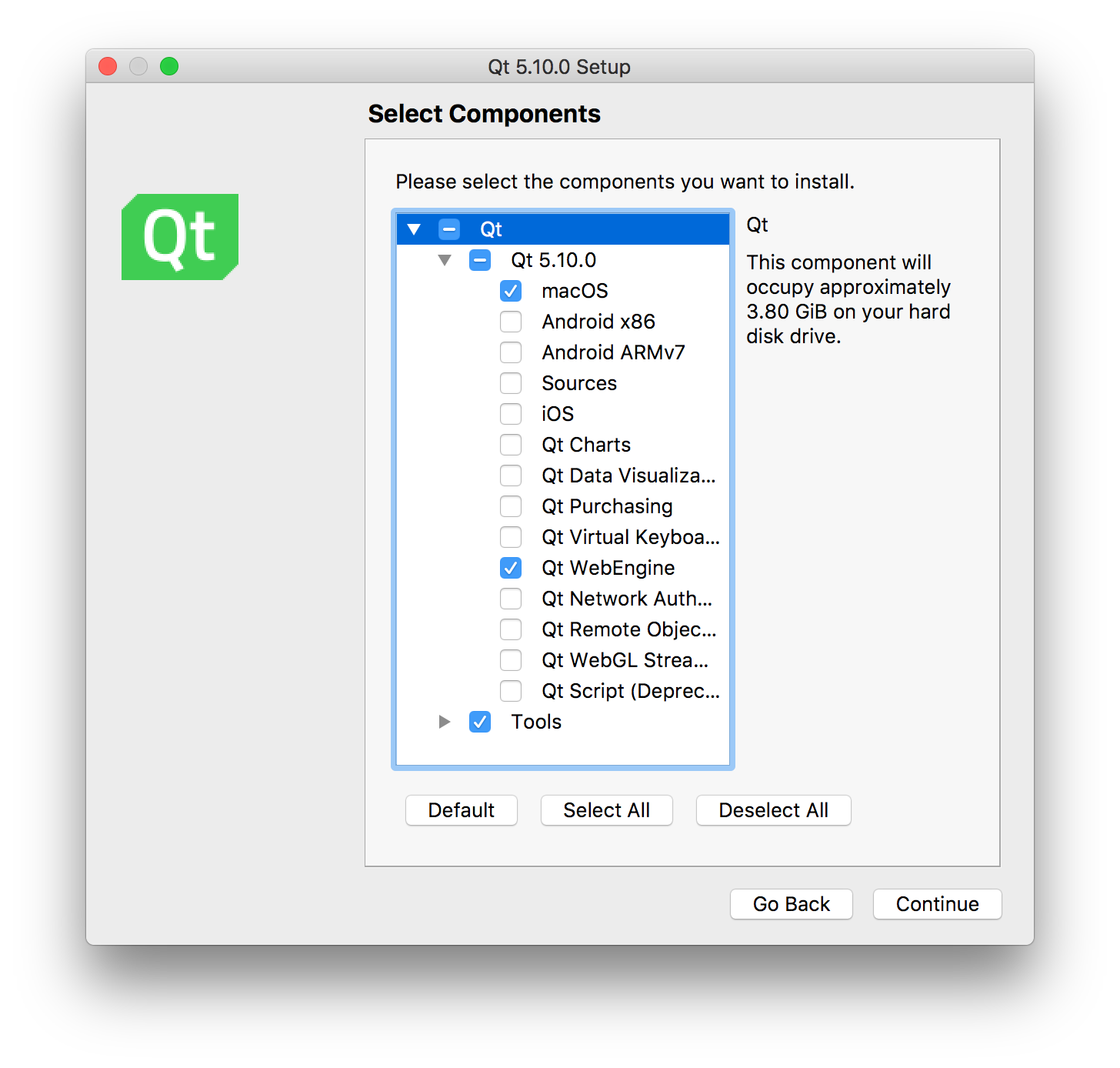
-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 208
Guide to Building JASP
The easiest way to build JASP is to use Qt Creator. After cloning the jasp-desktop project, open the JASP.pro file in the jasp-desktop directory, in Qt Creator. This project contains two runnable sub-projects, JASP-Desktop and JASP-Engine. In order to run JASP, JASP-Desktop is the correct project to run.
For those unfamiliar with using Qt Creator for development, there is some excellent documentation available here.
Alternatively, those that are more comfortable using command line tools can use QMake, the manual for which is available here. QMake projects (like JASP) are typically built in two steps; first QMake is called, which generates a Makefile for Make, and then Make is called with this generated Makefile.
We recommend building JASP in a separate directory to it's source directory. This can be achieved by calling QMake in a separate directory to the source, for example we might create a separate directory beside the jasp-desktop directory (perhaps called jasp-build), and then from this directory call:
qmake ../jasp-desktop/JASP.pro
make # -j8 # <- to gain a considerable speedup on a typical quadcore system
This generates the Makefile in the jasp-build directory, and all resulting object files and executables will be output to this directory.
JASP requires several dependencies which are documented below.
JASP depends on:
To be able to build JASP the listed dependencies are required and can be easily installed on your system through jasp-required-files Simply clone the git repository next to your jasp-desktop folder as follows:
[+] jasp-desktop < from github >
[+] jasp-required-files < from github >
Building JASP under windows is the most temperamental but should pose no large problems. After cloning the jasp-desktop and jasp-required-files repositories you must however install the following software:
- [Visual Studio 2017] (https://www.visualstudio.com/downloads/) Download community version
- [R Tools 34] (https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/Rtools/Rtools34.exe)
Besides this one needs to make a new kit in Qt Creator to be able to build JASP-R-Interface. To Do: Write a nice guide here that explains how to do it!
After cloning the jasp-desktop and jasp-required-files repositories you must however install the following software:
- Clone the JASP repository
- XCode Qt on OS X relies on XCode to function, you can install this through the App Store. It's easiest if you install this, run it, accept the license agreement, and then close it down before installing Qt.
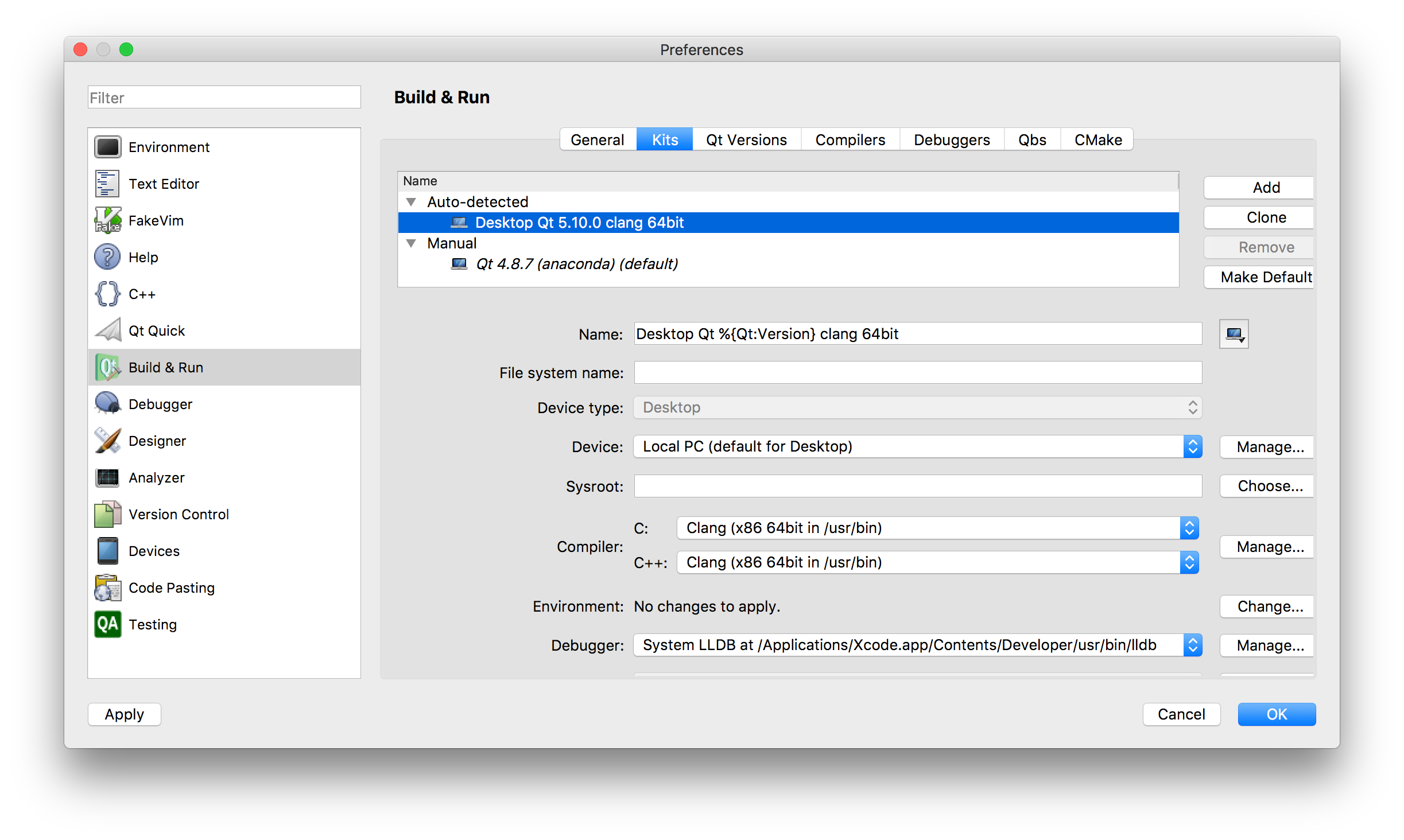
2.a. Configure Qt5.11.3: Left top menu: Qt Creator - Preference. Left menu: "Build & Run", tab: "Kits". Auto-detect should give "Desktop Qt 5.11.3 clang 64bit". Click on this. Choose the compiler Clang (x86 64bit in /usr/bin) for both C and C++.
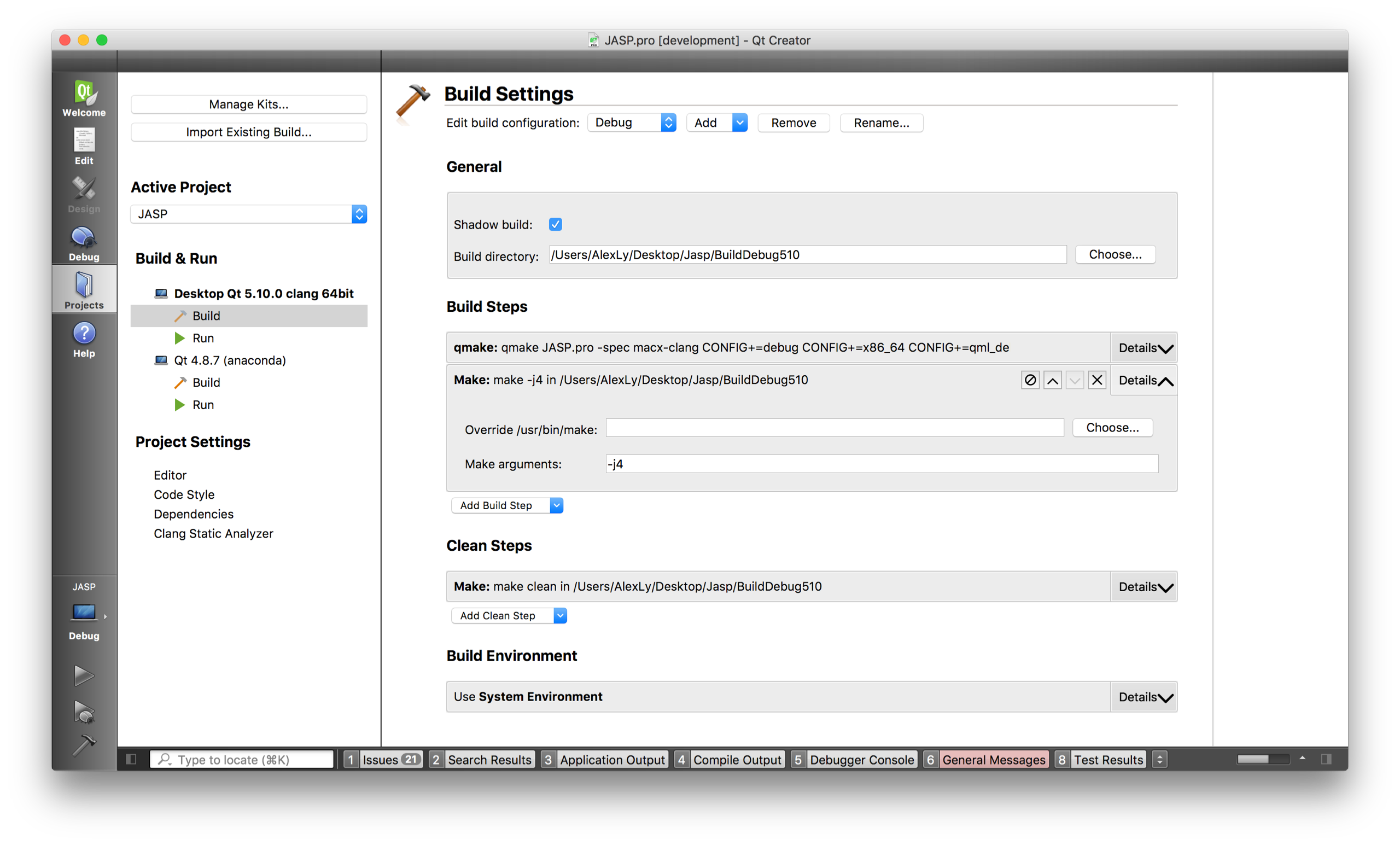
2.b. Configure project: Click "Projects" in the left ribbon and provide the "debug build" and "release build" folders with the correct compilers. This should look like:
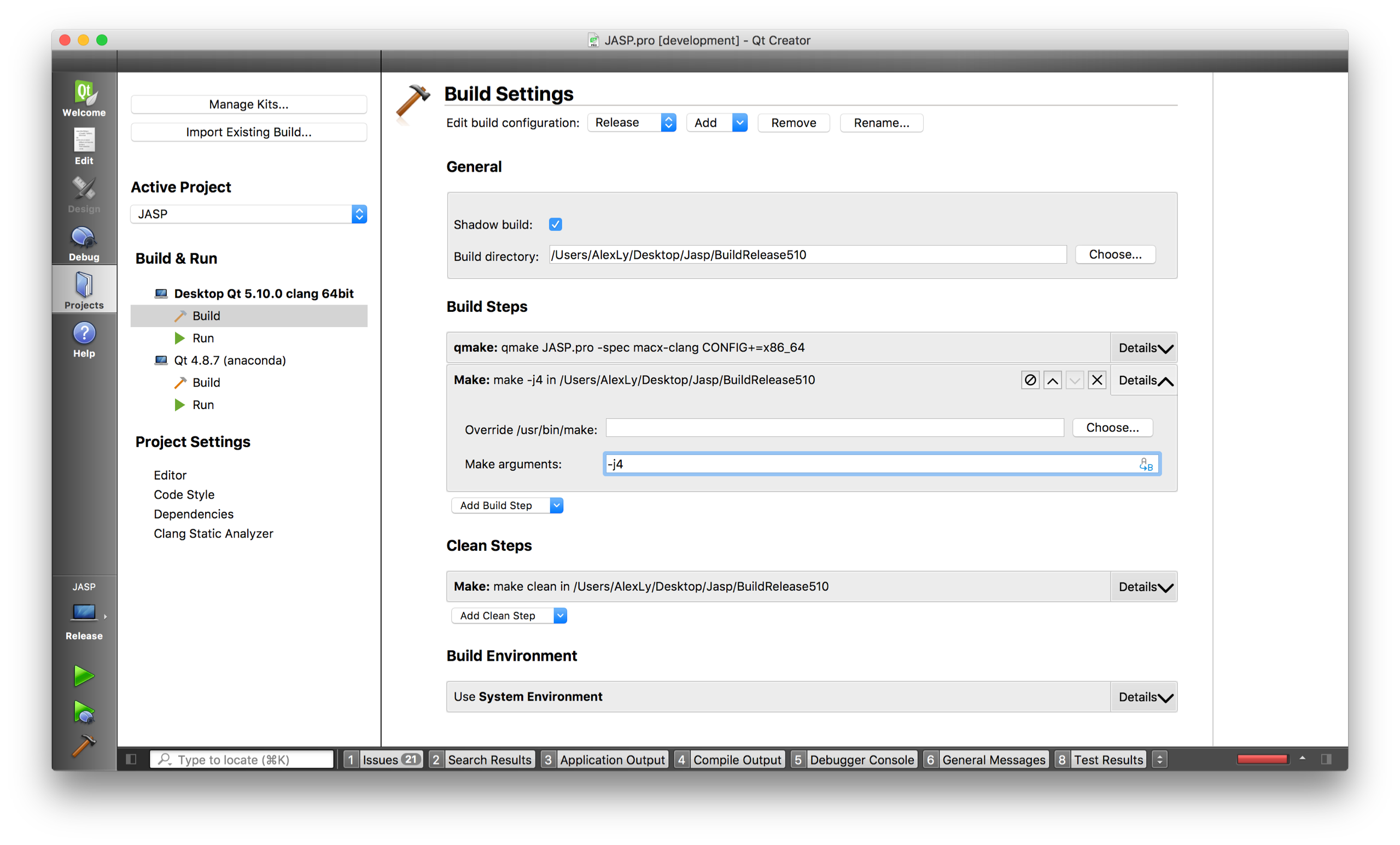
and like:
In both case, I've added the flag "-j4" to make use of all my four cores on my mac.
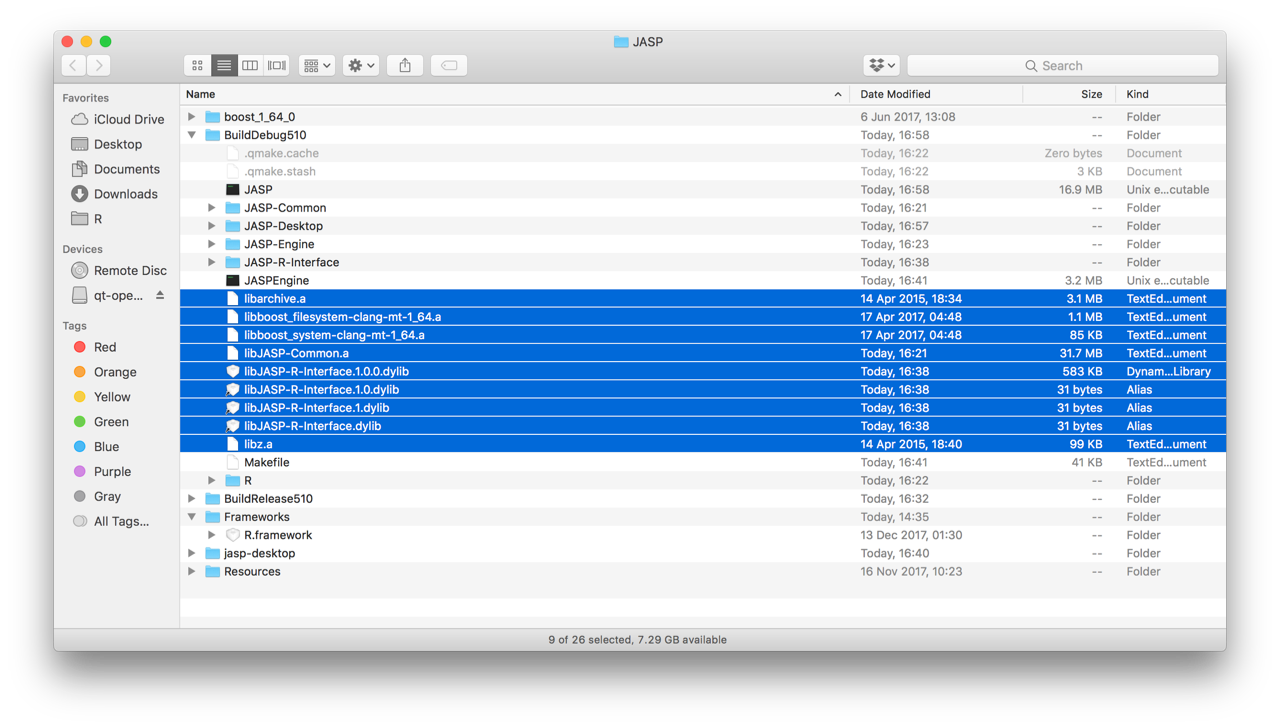
- In the end, your folder should be structured as follows:
where the blue files are the binaries that are added manually.
To build JASP under Ubuntu (17.10+), debian, and derivatives, you will need:
sudo apt-get install libboost-dev r-base-core r-cran-rcpp r-cran-rinside libqt5widgets5 qtwebengine5-dev libqt5webchannel5-dev libqt5svg5-dev qt5-qmake libarchive-dev libboost-filesystem-dev libboost-system-dev libjsoncpp-dev qt5-default qtcreator
Then you start qtcreator and open JASP.pro, run qmake and build all. After that you should be able to run JASP.
Under Fedora, you need these packages:
- qt-devel
- qt5-qtwebengine-devel (probably)
- qt5-qtwebchannel-devel (probably)
- boost-devel
- libarchive-devel
And (under fedora only), in R (started as root so packages are installed systemwide), you need to install:
install.packages(c("Rcpp","RInside"))
Finally, under Fedora only, you need to create a symlink so that R is found:
sudo ln -s /usr/lib64/R/ /usr/lib/R
In order to run, you will need (Ubuntu and alike):
sudo apt-get install libjsoncpp1 r-base-core r-cran-rcpp r-cran-rinside r-cran-bayesfactor r-cran-lme4 r-cran-afex r-cran-car r-cran-effects r-cran-logspline r-cran-lsmeans r-cran-plotrix r-cran-rjson r-cran-vcd r-cran-vcdextra r-cran-ggplot2 r-cran-hypergeo libqt5webenginewidgets5 libqt5webengine5 libqt5webenginecore5 libqt5svg5 openssl
It works under Fedora, if you install these R packages manually in R:
install.packages(c("BayesFactor","lme4","afex","car","effects","logspline","hypergeo","rjson"))